Introduction
Administration of the gateway is done through a web interface. All settings are accessible through an address on your local network.
Requirements
To access the web interface, you need the following:
An installed gateway device.
A computer connected to the LAN or WLAN port on the device.
A web browser installed on the computer.
The default address for the web interface is http://192.168.1.1.
Overview
Access web interface
To access the web interface you need to use your web browser. There are multiple ways of accessing the interface.
User Roles
The web interface uses Roles to provide and restrict access to the various features in the device.
There are four pre-defined roles: User, Support, Admin, and Root.
User Modes
In addition to User Roles, the User Modes may provide further constraints on what settings and features are displayed in the web interface.
Note: The mode affects display only, the features are still available and operational.
Features
Depending on your device and/or geographical region, certain features may be unavailable in the interface.
Applying changes
When you change a setting or a value in the interface, it gets added to a list of changes. The changes will not take effect until you click apply.
Access web interface
To access the web interface you need to use your web browser. There are multiple ways of accessing the interface.
IPv4
The standard IPv4 address for the interface is http://192.168.1.1.
Hostname
The web interface can be accessed through a default hostname, for example inteno.lan/ or routerlogin.net/, or through custom hostnames set up by the provider.
IPv6
An IPv6 address or IPv6 hostname can also be used to access the web GUI. The exact address will vary with your provider.
Open GUI
- Launch your web browser
- Enter the address (for example: http://192.168.1.1) / http://(inteno.lan/ or http://routerlogin.net/ / http://2001:0:0:0:DB8:800:200C:417A
- Press [Enter].
You are taken to the web interface login page.
Login
To login to the web interface, you use a user name and a password.
Configuration
(For default passwords see: User Roles).
Note: Your operator may have specified different passwords and user levels. If so, you need to request those from your operator.
Log in to the web interface:
- Enter a user name
- Enter the password
- Click OK.
You are taken to the web interface Overview page.
User Modes
In addition to User Roles, the User Modes may provide further constraints on what settings and features are displayed in the web interface.
Note: The mode affects display only, the features are still available and operational.
Overview
Basic Mode
Basic mode provides access to a selected set of settings and aspects of features, displaying a reduced set of options. This mode is suitable for the most common tasks and configurations.
Expert Mode
Expert mode provides access to a larger number of settings and aspects of features. This mode is suitable when you have deeper technical knowledge and want to do specific customizations or troubleshooting.
Basic Mode
Basic mode provides access to a selected set of settings and aspects of features, displaying a reduced set of options. This mode is suitable for the most common tasks and configurations.
Features
In basic mode, all Expert mode settings and views are hidden from the interface. However, if you select a particular task in basic mode that requires expert mode settings, they will automatically be displayed.
Expert Mode
Expert mode provides access to a larger number of settings and aspects of features. This mode is suitable when you have deeper technical knowledge and want to do specific customizations or troubleshooting.
Features
In expert mode, all Basic mode settings and views are also shown.
User Roles
The web interface uses Roles to provide and restrict access to the various features in the device.
There are four pre-defined roles: User, Support, Admin, and Root.
User
The User role has restricted access to basic set of features.
login: user
password: user
Support
The Support role has elevated access to basic and a set of advanced features.
login: support
password:support
Admin
The Admin role has unrestricted access to all basic and advanced features.
login: admin
password:admin
Root
The Root role has unrestricted access to the device, and can be used for command line access to the device via ssh.
login: root
password:root
Features
Depending on your device and/or geographical region, certain features may be unavailable in the interface.
Availability
Certain features may not be available in your interface, depending on several factors:
Device - Your device may be limited in which ports are avaible.
Geographical region - Features might not be offered in some regions or countries.
Operator Settings - Your operator may have restricted, altered or added features in the software.
Applying changes
When you change a setting or a value in the interface, it gets added to a list of changes. The changes will not take effect until you click apply.
Configuration
The unapplied changes and apply button are shown at the bottom of the window.

To make the changes take effect click Apply.
To keep the current state without any changes click Cancel.
Overview
The Overview page shows the most important statuses and settings for your device.
Parts
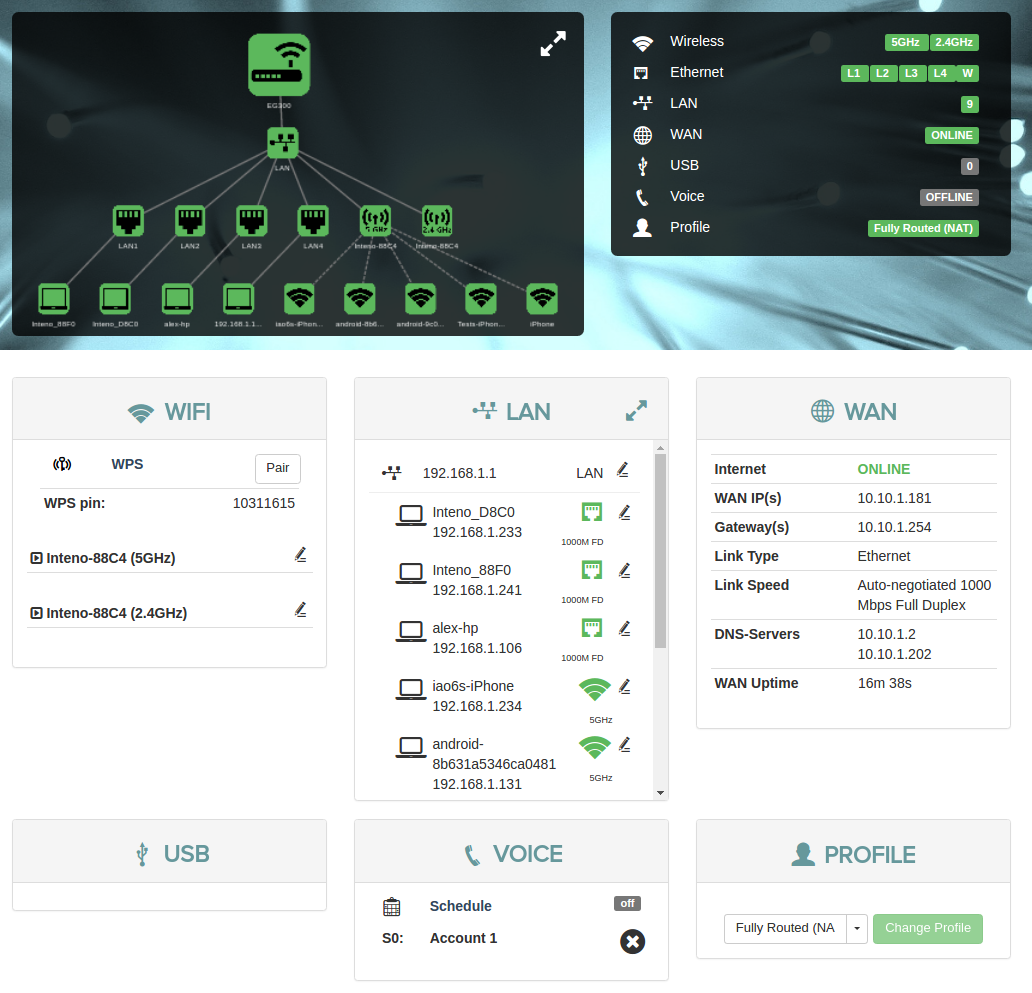
The overview has three parts: a device network map, configuration shortcuts, and status panels.
Device Network Map
The device map shows how your device is connected to the LAN and the WAN, as well as other devices in the local network.
Configuration Shortcuts
The configurations show status for and provide shortcuts provide quick access to various common settings.
Status Panels
The status panels display status information about selected features. They also allow you quick access to configuration of the most common features.
Device Network Map
The device map shows how your device is connected to the LAN and the WAN, as well as other devices in the local network.
View
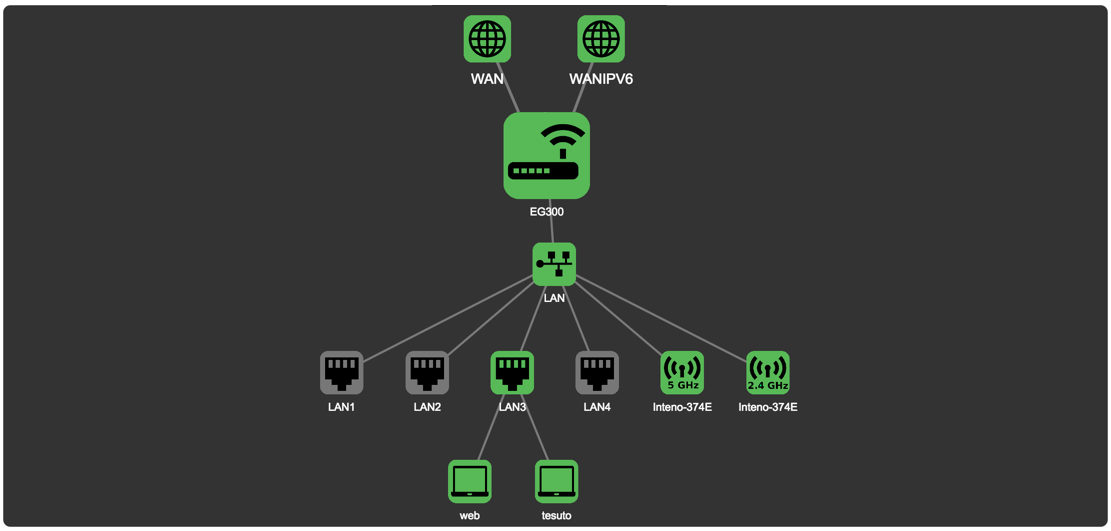
Colors
The status of a device is indicated by the color of the icon.
| Color | Status |
|---|---|
| Green | Enabled and active |
| Black | Enabled, not active |
| Yellow | Active, with warnings. |
| Red | Active, not functional. |
Details
More detailed Information about the status of an item in the map is availabe by pointing the cursor at an icon in the map.
View
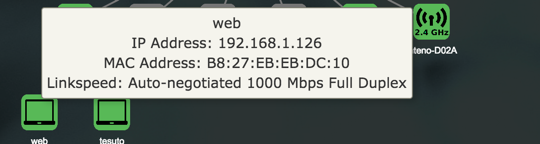
The information displayed in the popups varies with the item being viewed.
WAN
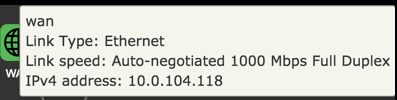
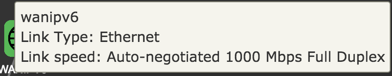
Device
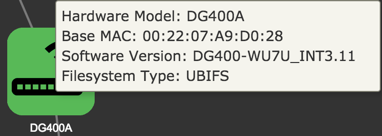
LAN

Port

Wifi
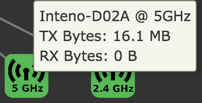
Client
Configuration Shortcuts
The configurations show status for and provide shortcuts provide quick access to various common settings.
Configuration
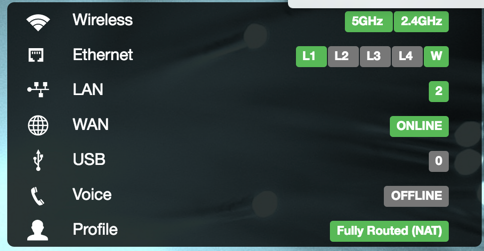
| Option | |
|---|---|
| Wireless | Active wireless radios. |
| Ethernet | LAN ports in use on the device. |
| LAN | Active LAN |
| WAN | Status of WAN connection. |
| USB | Connected USB devices, if any. |
| Voice | Voice port status, if any. |
| Profile | Selected network profile, if any. |
Status Panels
The status panels display status information about selected features. They also allow you quick access to configuration of the most common features.
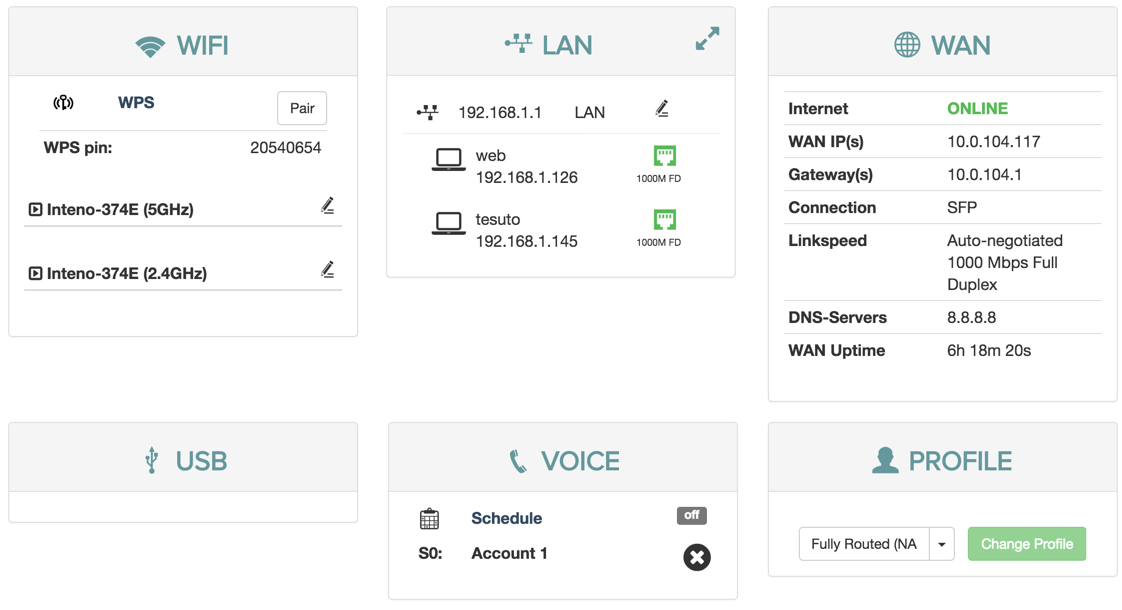
WIFI
The WiFi status panel lets you change the default wireless security settings to make your network more secure.
You can also view the wifi status and edit the wireless interface.
Additonally, you can WPS to set up clients.
LAN
WIFI
The WiFi status panel lets you change the default wireless security settings to make your network more secure.
You can also view the wifi status and edit the wireless interface.
Additonally, you can WPS to set up clients.
View
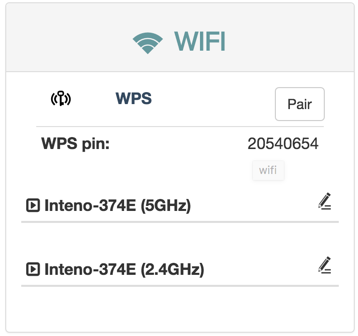
WPS settings
WPS makes it easier to connect other wireless devices to your device on an encrypted channel.
Edit 5GHz Wireless Interface
In the edit wireless interface view you can change different aspects of your interface.
Edit 2.4GHz Wireless Interface
In the edit wireless interface view you can change different aspects of your interface.
WPS settings
WPS makes it easier to connect other wireless devices to your device on an encrypted channel.
Edit 2.4GHz Wireless Interface
In the edit wireless interface view you can change different aspects of your interface.
Configuration
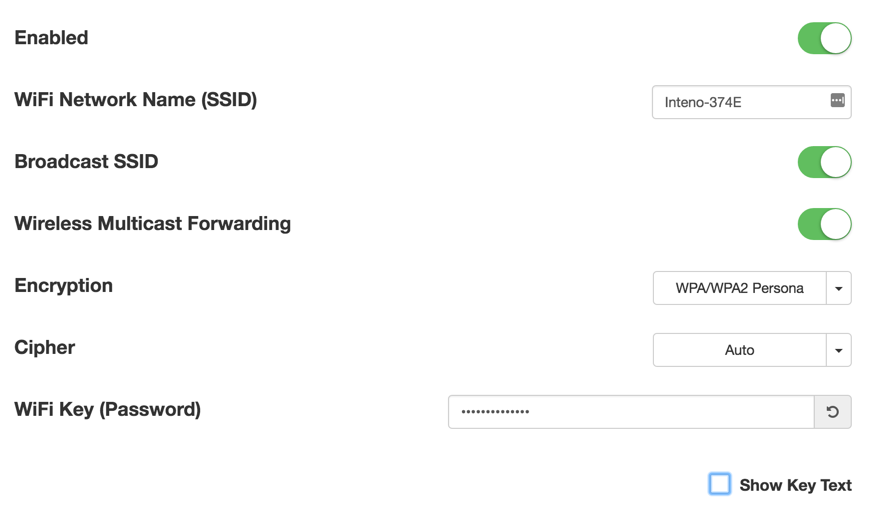
Wireless Settings
To open The wifi status view for 2.4GHZ:
- Click 2.4 GHz to open the wifi status view
To edit the wireless interface for a radio:
- Click the
 edit button to open up the wireless interface settings
edit button to open up the wireless interface settings
- Edit the wireless interface
- Click Save
Edit 5GHz Wireless Interface
In the edit wireless interface view you can change different aspects of your interface.
Configuration
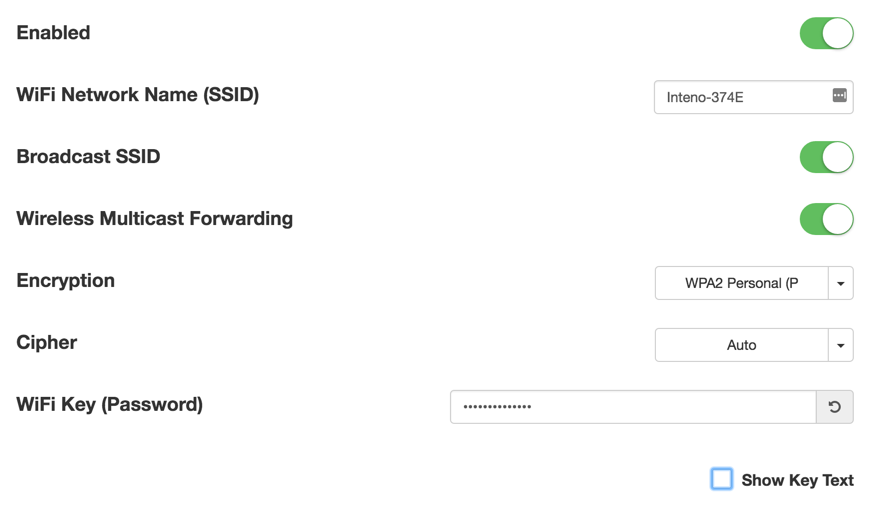
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Toggle interface on or off. |
| WiFi Network Name | Edit name of SSID network. |
| Broadcast SSID | Toggle to make the network SSID visible or invisible. |
| Encryption | Selected encryption method. |
| Cipher | Form of Cipher. |
| WiFi Key (Password) | Text to use as wifi key. |
| Show Key Text | Displays the wifi key text. |
Wireless Settings
To open the wifi status view for GHZ:
- Click 5GHz to open the wifi status view
To edit the wireless interface for a radio:
- Click the
 edit button to open up the wireless interface settings
edit button to open up the wireless interface settings
- Edit the wireless interface
- Click Save
LAN
The LAN panel shows basic information about the device and connected clients IP addresses.
From the LAN status panel you can configure the DHCP settings for the device.
Configuration
To open the Edit LAN Settings dialog, click the ![]() edit button.
edit button.
To view a more detailed overview of the clients, click the ![]() expand button
expand button
To view details about a client click the client in the list.
Overview
Detailed Client Overview
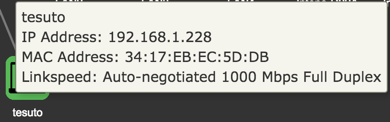
In The Detailed Client Overview, information about the clients in the LAN is displayed.
Edit LAN Settings
In The Edit LAN settings view you can change different features about your network.
Client
The Client dialog displays information about the connected clients and allows you to edit their configuration.
Detailed Client Overview
In The Detailed Client Overview, information about the clients in the LAN is displayed.

| Item | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Hostname | Client hostname. | |
| IP Address | Client IPv4. | |
| MAC Address | Client MAC Address . | |
| Port | Device port. | |
| Network | Network interface for the client. | |
| Link Speed | Type of negotiation, speed and duplex for the connection. |
Edit LAN Settings
In The Edit LAN settings view you can change different features about your network.
Configuration
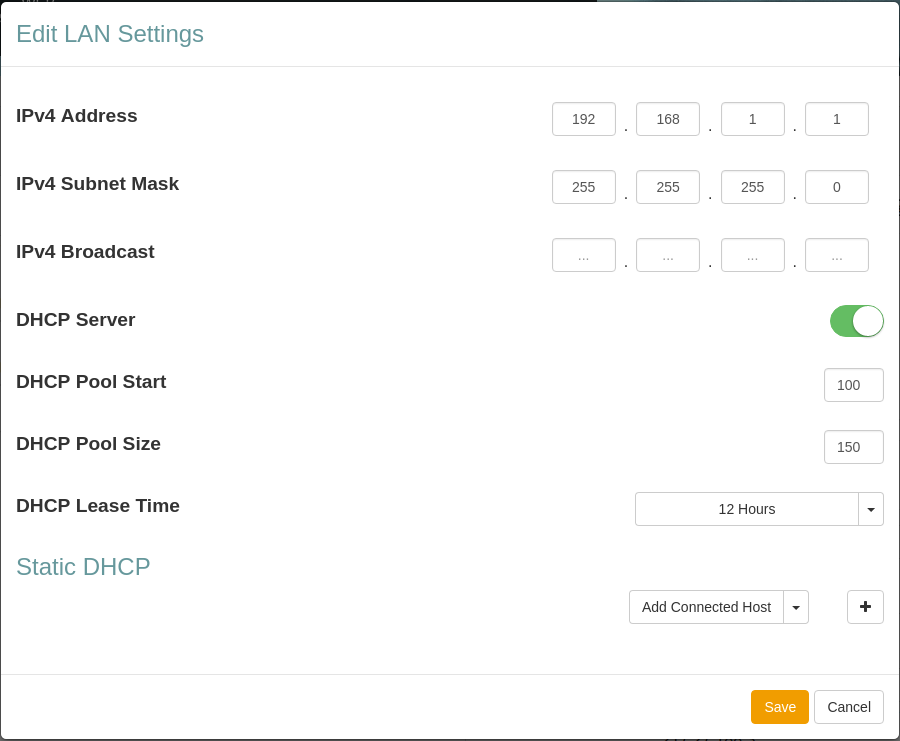
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | Device DHCP address |
| IPv4 Subnet Mask | IPv4 Subnet Mask |
| IPv4 Broadcast Mask | IPv4 Broadcast Mask |
| DHCP Server | Turn DHCP Server on or off. |
| DHCP Pool Start | Start IP number for the DHCP Pool start number IP address |
| DHCP Pool Size | Number of IP addresses in the DHCP Pool |
| DHCP Lease Time | DHCP Lease Time for the LAN. |
| Static DHCP | Reserve an IP address DHCP Lease for a connected device. |
Static DHCP
The Static DHCP section lets you configure IP address DHCP Leases for connected devices.
Configuration
Add Static DHCP Lease
To add a static DHCP lease:
- Add an existing client or create a lease from scratch:
- To select an existing client:
- Click Add connected host to open the list
- Select the desired client
- Click the
 add button
add button
- To add a static DHCP lease manually:
- Only click the
 add button
add button
The information for existing client is added automatically.
- Add or edit the client information as neeed.
- Click Save
Client
The Client dialog displays information about the connected clients and allows you to edit their configuration.
View
Information about the client is divided into several tabs.
Overview
Port Forwarding
In the Port Forwarding tab you can map incoming connections on different ports to ports on the client.
Static Leases
The Static Leases tab allows you to assign a static IP address dhcp lease to the client.
Realtime Graphs
The Realtime Graphs view provides access to graphical representations of status for the device. The graphs scroll as time progresses and lines indicate the current status.
WiFi Realtime Graphs
For WiFi clients (it is not shown for regular LAN clients), the Realtime Graphs tab you can map incoming connections on different ports to ports on the client.
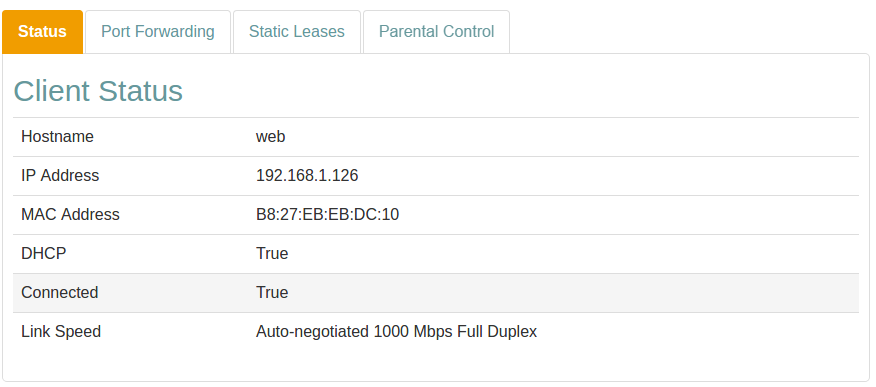
Status
The Status tab shows information about the client and the connection.
Status Information
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Hostname | The client Hostname. |
| IP Address | Assigned IP address. |
| MAC Address | MAC address. |
| DHCP | DHCP status. |
| Connected | Connection status. |
| Link Speed | Type of negotiation, speed and duplex for the connection. |
Wireless Details
For WiFi clients, the Wireless Details section shows detailed information about the wireless connection. All data is measured since last downtime.
| Item | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | WiFi frequency band for the access point. | 2.4GHz |
| RSSI | RSSI strength for the signal. | -64 dBm |
| SNR | Signal-To-Noise-Ratio. | 21 dBm |
| Idle | Time idle. | 1 s |
| In Network | Time in network. | 1813 s |
| WME | Status of WMM. | True |
| Power Save | Is Power save enabled? | False |
| N Mode | Is 802_11n supported? | True |
| VHT Mode | Is 802_11ac supported? | False |
| TX Bytes | Transmitted bytes. | 2438426 |
| RX Bytes | Recieved bytes. | 347988 |
| TX Rate | Transmission rate. | 58 Mbps |
| RX Rate | Recieve rate. | 6 Mbps |
Port Forwarding
In the Port Forwarding tab you can map incoming connections on different ports to ports on the client.
Mapping Section
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Port name. |
| Excluded ports | Protected ports that can't be mapped. |
| Public port | Public (external) port. |
| Private port | Private (client) port. |
| Protocol | Protocol. |
Protocol
The protocol setting filters traffic by protocol for the port forward.
Mapping Settings
To map incoming connections:
- Click Add mapping to open the mapping section
The mapping section lets you add configuration settings for the mapping.
Ports can be added one by one (80), as comma-separated lists (8080, 8090) or as ranges (21-22).
- Add information:
- Add a name as identification
- Add ports:
- Add public/incoming port(s)
- Add private/client port(s)
- Select protocol
- Click Save
- Click Close
Your information has now been saved and is visible in the mapping list.
Static Leases
The Static Leases tab allows you to assign a static IP address dhcp lease to the client.
Static Leases Section
Static Leases Settings
To assign a static address to the client:
- Click the
 add button to open the section
add button to open the section
- Add information for the type of network(s) you use
Parental Control
Parental control is used to restrict access to the network for particular devices.
Internet Access Scheduling
Parental control is handled by setting schedules where access is restricted to explicitly named MAC addresses.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Weekdays | List of days the filter applies. |
| Start Time | Time of day to start filtering. |
| Stop Time | Time of day to stop filtering. |
| | Edit filtering rule. |
| | Delete filtering rule. |
Add Parental Control
The Internet Access Schedule rules you add from the client panel will only apply to that client.
Internet Access Scheduling
Parental control is handled by setting schedules where access is restricted to explicitly named MAC addresses.
When adding a parental control filter from the client panel, the MAC Address is automatically selected from the client.
Add an Internet Access Schedule
- Select a Time Frame from the menu
- Edit the selected Days as needed
- Enter a time:
- From
- To
- Click Save
- Click Close
Start and Stop Times
The start time for a rule has to be lower than the end time.
If you want to have a rule that goes over midnight, you need to add two rules, one up until midnight, and one from midnight to when you want the rule to end.
For example:
Rule one: From 21:00 To 23:59
Rule two: From 00:00 To 06:00
A single rule of From 21:00 To 06:00 will not be saved.
WiFi Realtime Graphs
For WiFi clients (it is not shown for regular LAN clients), the Realtime Graphs tab you can map incoming connections on different ports to ports on the client.
Graph
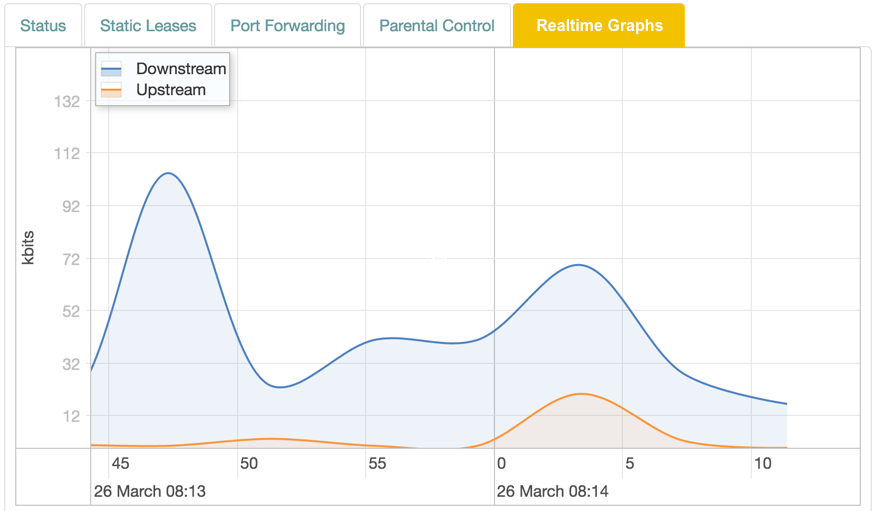
The display is shown in realtime, with lines representing traffic in kbit/s:
| Color | Traffic |
|---|---|
| Blue | Downstream. |
| Red | Upstream. |
Table
The table below the graph displays collected data since the tab was opened, and the total connection uptime since last downtime.
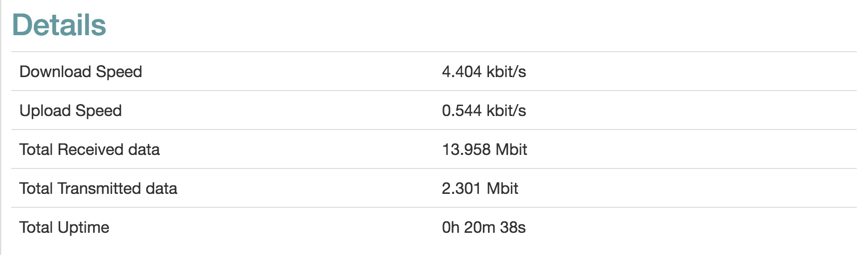
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Download Speed | Current download speed. |
| Upload Speed | Current upload speed. |
| Total Received Data | Downloaded data since the tab was opened. |
| Total Transmitted Data | Transmitted data since the tab was opened. |
| Total Uptime | Connection uptime since last downtime. |
Realtime Graphs
The Realtime Graphs view provides access to graphical representations of status for the device. The graphs scroll as time progresses and lines indicate the current status.
Overview
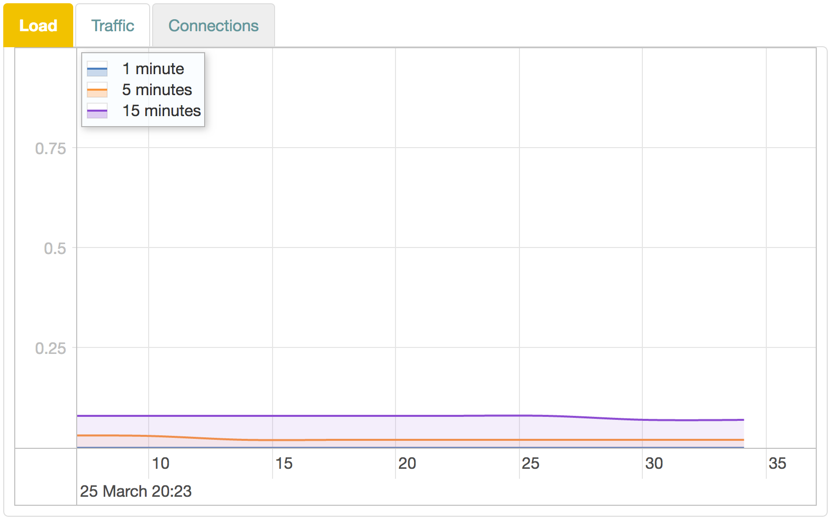
Load
The Load graph shows device load averages for different time recent periods.
Graph Lines
The display is shown in realtime, and the lines represent the average over different intervals:
| Color | Time |
|---|---|
| Blue | 1 minute |
| Red | 5 minutes |
| Purple | 15 minutes |
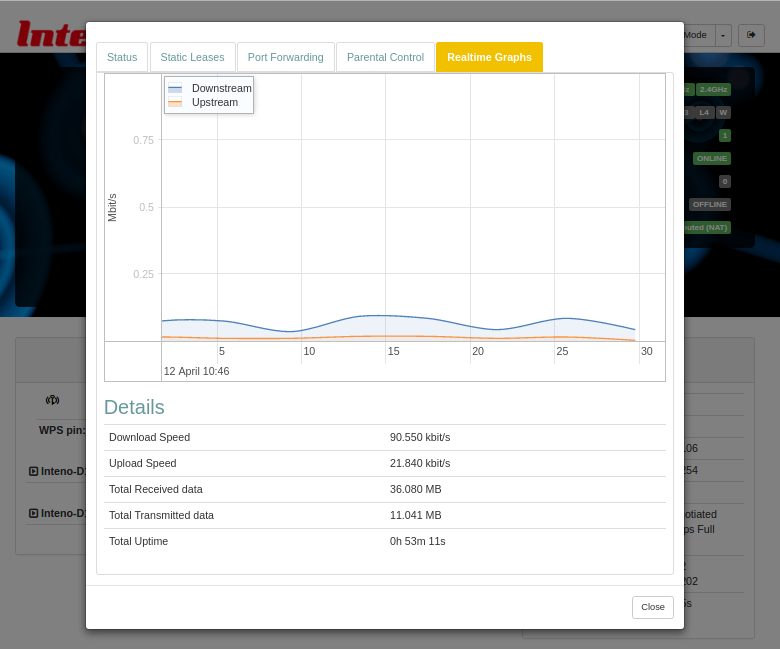
Traffic
The Traffic graph shows upload and download traffic for the interfaces.
Graph Lines
Each interface is available in its own tab. The display is shown in realtime, with lines representing traffic in kbit/s:
| Color | Traffic |
|---|---|
| Blue | Downstream. |
| Red | Upstream. |
WAN
Configuration
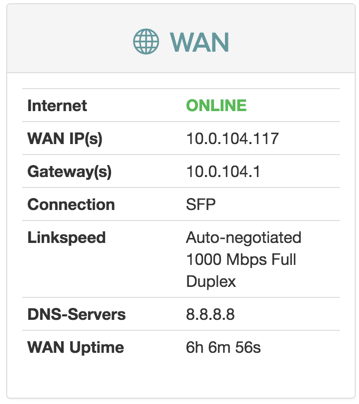
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Internet | Status of Internet connection. |
| Link | Status of link. |
| WAN IP(s) | IPv4 and IPv6 address to the device. |
| Gateway(s) | IPv4 and IPv6 address to gateway. |
| Link Type | Ethernet |
| Link Speed | Auto-negotiated 1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| DNS-Servers | IPv4 and IPV6 addresses to DNS servers. |
| WAN uptime | Time since last disconnect for IPv4 and IPV6 WAN connection. |
Voice
The Voice panel shows the status of the ringing schedule connected phone lines.
The Voice panel is not available in certain regions.
Profile
The Profile panel shows the network profiles configured on your device, if any.
The network profiles are configured by the manufacturer for each device type.
Depending on the network profile selected, additional panels may be displayed in the overview.
Voice
The Voice provides access to settings relating to voice communications through the device.
Overview
Voice Lines
The Voice Lines view shows a list of available voice lines for the device and allows you to configure them.
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings view contains advanced settings for SIP , voice lines and dial plans.
Number Blocking
The Number Blocking view allows you to block outgoing calls to specific numbers or or number ranges.
Ringing Schedule
The Ringing Schedule view lets you define when telephones should be allowed to ring.
Speed Dialing
The Speed Dialing view lets you configure a set of shortcode numbers that convert to the specified numbers when dialled.
Call Log
The Call Log view shows a list of the recent calls handled through the device.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Date | Date for the call. |
| Time | Time for the call. |
| External Number | Calling number. |
| Internal Number | Receiving number. |
| Duration | Duration of the call. |
SIP Accounts
The SIP Accounts view shows information about configured SIP accounts for the device.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of selectable accounts.
When a particular account is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn account on or off. |
| Account Name | Name of SIP account. |
| SIP domain name | Name of SIP domain. |
| SIP Username | The SIP account username for the account. |
| SIP Authentication Name | SIP Authentication Name used with password to register with SIP server. |
| SIP Password | Enter new password to change. |
| Show Key Text | Display the password. |
| Display Name | Display name used in Caller ID. |
| SIP Server/Registrar | Address for SIP server. |
| SIP Server/Registrar Port | Port for SIP server. |
| SIP Outbound Proxy | Address for outbound proxy. |
| SIP Outbound Proxy Port | Port for outbound proxy. |
| Incoming Phone Lines | Check boxes for connected phone line ports. |
| Preferred codecs | Order of preference for SIP codecs. |
| G.711MuLaw Packetization | Packetization setting for G.711MuLaw. |
| G.726 Packetization | Packetization setting for G.726. |
| G.729a Packetization | Packetization setting for G.711ALaw. |
| G.G.729a Packetization | Packetization setting for G.729a. |
| Autoframing | Negotiate packetization when call is established. |
| SIP Transport | UDP / TCP / TLS |
| Encryption | Use Secure Real-time Transport Protocol. |
| Use as Fax | Indicate that this SIP account will be used for a fax machine. This will force some settings. |
| Mailbox | Voicemail inbox. |
Add account
You can add as many accounts as you needed.
To add a account:
- Click the Add button
- Enter a Name for the account
- Enter values as needed.
- Click Apply
SIP Users
The SIP Users view shows information about configured SIP users for the device.
View
At the top of the page is a list of selectable accounts.
When a particular account is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn user on or off. |
| Name | Display name used in Caller ID. |
| Extension | Extension for this user. |
| User Name | SIP user name. |
| User Password | Enter new password to change. |
| Show Key Text | Display the password. |
| Call out using SIP provider | SIP account for outbound calls. |
| Mailbox | Voicemail inbox. |
| Preferred codecs | Order of preference for SIP codecs. |
| Host | Specific host for this user. |
| Qualify | Check that the user is reachable. |
Add user
You can add as many users as you needed.
To add a user:
- Click the Add button
- Enter a Name for the user
- Enter values as needed.
- Click Apply
Voice Lines
The Voice Lines view shows a list of available voice lines for the device and allows you to configure them.
Each available voice line has its own panel. Detailed information about each line is shown when you expand the panel.
The panels allow you to configure individual voice lines.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Identifier for the DECT line. |
| Internal Number | Diect call number. |
| Outgoing Calls Number | SIP account for external calls. |
| Call Waiting | Enable call waiting notification. |
| Call ID Restriction | Hide caller ID. |
| Voice Activity Detection | Detect voice (Transparent / Aggressive / Conservative). |
| Comfort Noise Generation | Generated noise (White / Hot / Spectrum estimate). |
| Echo cancellation | Remove echoes. |
| Transmit gain | Increase transmitted signal. |
| Receive gain | Increase received signal. |
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings view contains advanced settings for SIP , voice lines and dial plans.
Overview
Advanced SIP Settings
The Advanced SIP Settings view lets you configure detailed parameters for your SIP services.
Advanced Line Settings
The Advanced Line Settings view lets you configure detailed parameters for your voice lines .
Custom Dial Plan
The Custom Dial plan view allows you to configure dialling digits for various services and networks.
Advanced SIP Settings
The Advanced SIP Settings view lets you configure detailed parameters for your SIP services.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Sip Proxy servers | Proxies to allow incoming calls from. |
| Bind Interface | Restrict listening to particular WAN interface. |
| Bindport | Port to use for UDP listening. |
| User Agent | Custom User-Agent information in the SIP header. |
| RTP Port Range | Ports to use for RTP |
| DTMF Mode | Mode for DTMF (Compatibility / RFC 2833 / SIP INFO / Inband). |
| Register Interval | Time in seconds between registration attempts. |
| Realm | SIP Realm for digest authentication. |
| Localnet | Network addresses that are considered inside of the NAT network. |
| Register Attempts | Number of registration attempts before giving up. |
| Register Timeout | Time before giving up a registration attempt. |
| Register Back-off Attempts | Number of attempts before back-off. |
| Register Back-off Timeout | Time in back-off before giving up attempt to register. |
| Remote Hold | Send hold events to proxy (Let network handle music on hold). |
| SRV Lookup | Enable DNS SRV lookup. |
| DNS Manager | Enable Asterisk DNS manager. |
| DNS Manager Refresh Interval | Refresh interval for the DNS manager. |
| Line suffix in contact header | Add suffix to SIP contact header with information about called lines. |
| SIP DiffServ | Differentiated services type of service for SIP data. |
| Audio DiffServ | Differentiated services type of service for audio data. |
| Congestion tone | Tone to play on congestion. (Congestion / Info) |
| STUN server | STUN service provider. |
| TLS/SSL Version | TLS v1 / TLS v2 / TLS v3. |
| Cipher string | Cipher identifier string. |
| Trusted CA | Public key for a trusted Certificate Authority. |
Trusted CA Certificate
To add a Trusted CA Certificate key:
- Click Add
- Copy the public key
- Paste the key into the window
- Click Save
- Click Apply
Advanced Line Settings
The Advanced Line Settings view lets you configure detailed parameters for your voice lines .
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Locale selection | Country for device location. |
| Enable Jitter Buffer | Turn jitter prevention buffer on or off. |
| Force Jitter Buffer | Forces the receiver to use a jitter buffer. |
| Jitter Buffer implementation | The type of jitter buffer Fixed / Adaptive. |
| Maximum Jitter Buffer size | Size of jitter buffer (ms). |
| Enable Packet Loss Concealment | Turn PLC on or off. |
| Inter-digit timeout | Time between dialled digits before timing out (ms). |
Custom Dial Plan
The Custom Dial plan view allows you to configure dialling digits for various services and networks.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable incoming | Turn dial plan on or off for incoming calls. |
| Enable outgoing | Turn dial plan on or off for outgoing calls. |
| Enable custom hangup | Turn custom hang up on or off. |
| All Ports Extension | Port test extension. |
| Test Audio Extension | Audo tests the audio quality. |
| Test Echo Extension | Echo returns the outgoing audio from a channel back to the channel. |
Number Blocking
The Number Blocking view allows you to block outgoing calls to specific numbers or or number ranges.
Outgoing
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Outgoing Number Blocking | Turn blocking on or off for outgoing calls. |
| Do not allow connections to these numbers | List of blocked numbers. |
| Block connections to all foreign numbers | Block calls to different locales. |
| Block connections to all special rate numbers | Block calls to premium rate or pay services. |
Incoming
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Incoming Number Blocking | Turn blocking on or off for incoming calls. |
| Do not allow connections from these numbers | List of blocked numbers. |
Block number
To block a number:
- Click the
 add button
add button - Click in the Phone extension box
- Enter the number
- Click outside of the Phone extension box
- Click Apply
Block number range
You can use # as wildcard to define number ranges. For example “0160#” blocks all numbers starting with “0160”.
To block a sequence of numbers:
- Click the
 add button
add button - Enter digits
- Add '#' as wildcard
- Enter the number
- Click outside of the Phone extension box
- Click Apply
Ringing Schedule
The Ringing Schedule view lets you define when telephones should be allowed to ring.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Ringing Schedule | Turn the schedule on or off. |
| During the times below ringing is | Enabled / Disabled. |
| Day | List of days when status applies. |
| Time | Time interval when status applies. |
| Status | Enabled / Disabled. |
Speed Dialing
The Speed Dialing view lets you configure a set of shortcode numbers that convert to the specified numbers when dialled.
The speed dialling list consists of the numbers 0 to 9. For each of these, you can add a number or extension that will be called when somebody dials the number.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed Dialing | Turn speed dialling on or off. |
| Remove all entries from speed dial list | Clears the list |
DECT Radio
The Dect Radio view allows you to configure DECT radio settings.
Configuration
Network
The Network view provides access to the devices, connections and available configurations in the network.
Overview
Connections
The Connections view allows you configure various connection interfaces to use in your device.
Routes
Static routes are useful if you have several networks accessible from your router and you want to correctly route packets between them.
Firewall
The firewall lets you filter traffic, set up port forwarding or expose particular services to the outside world.
Quality Of Service
The Quality Of Service view allows you to configure parameters for Quality of Service through applying groups of classes to interfaces.
MultiWAN
The MultiWAN view allows you to create and configure WAN traffic divisions for load balancing and failover and applying traffic rules.
Devices
The Devices view allows you to configure settings for various network types.
Overview
Ethernet Ports
The Ethernet Ports view allows you to configure the physical ethernet interfaces of your device.
Base Device
The Base Device view shows you a list of devices that are used to access the network.
Configuration
Device Status
The status of a device is indicated by the color of the icon.
| Color | Status |
|---|---|
| Green | Enabled and active |
| Black | Enabled, not active |
Note: These are the default colors. Your operator may use a different coloring scheme.
Ethernet Ports
The Ethernet Ports view allows you to configure the physical ethernet interfaces of your device.
Configuration
Interfaces
At the top of the page is a list of selectable ethernet port devices.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Port Speed | Configuration of transmission speed, port speed. |
Uplink
Below the ethernet interface list you can find the uplink setting.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Uplink Port | Select uplink interface. |
Overview
Edit Interface Device
The Edit button next to each interface allows you to edit the parameters for the interface.
Uplink
The Uplink section view allows you to select which interface to use as uplink for the device.
Edit Interface Device
The Edit button next to each interface allows you to edit the parameters for the interface.
Configuration
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Port Speed | Configuration of transmission speed, duplex setting and auto-negotiation. |
| Pause Frame | Enable Pause Frame for flow control. |
Port Speed
In the Port Speed dropdown, you can select a combination of duplex setting and auto-negotiation settings for the interface.
| Option | Comment |
|---|---|
| Full auto-negotiation | Applies to both auto-negotiation and duplex setting. |
| Max 100Mb auto-negotiation, full duplex. | |
| Max 100Mb auto-negotiation, half duplex. | |
| Max 10Mb auto-negotiation, full duplex. | |
| Max 10Mb auto-negotiation, half duplex. | |
| Only 100Mb, full duplex. | |
| Only 100Mb, half duplex. | |
| Only 10Mb, full duplex. | |
| Only 10Mb, half duplex. | |
| Disabled | Interface is disabled. |
Uplink
The Uplink section view allows you to select which interface to use as uplink for the device.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of selectable ethernet port devices.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Uplink | Port to use as uplink for the device. |
Note: Selecting None will disable uplink traffic.
ADSL
The ADSL view allows you to configure ADSL devices.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of selectable devices.
When a particular device is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the device. |
| VPI | ATM Virtual Path Identifier. |
| VCI | ATM Virtual Channel Identifier. |
| DSL Link Type | EoA / PPPoE / IPoE. |
| Encapsulation Mode | LLC SNAP / VC-MUX. |
| Service Type | Service Type. |
| Bridge | Setting to enable network bridge use. |
Service Type
Service types define the guaranteed level of service in a ATM network. This involves such things as the timing between the source and destination, the guaranteed bandwidth and how many cells get lost in transmission.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| UBR without PCR | Use Unspecified Bit Rate without Peak Cell Rate. |
| UBR with PCR | Use Unspecified Bit Rate with Peak Cell Rate. |
| CBR | Use Constant Bit Rate. |
| Non-Realtime VBR | Use Non-Real-Time Variable Bit Rate. |
| Realtime VBR | Use Real-Time Variable Bit Rate. |
VDSL
The VDSL view allows you to configure VDSL devices.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of selectable devices.
When a particular device is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the device. |
| DSL Latency Path | DSL Latency Path 1, 2 or both 1 & 2. |
| PTM Priority | Normal or High PTM Priority . |
| IP QoS Schedule Algorithm | Strict Priority Precedence / Weighted Fair Queuing. |
| Bridge | Setting to enable network bridge use. |
Latency Path
The DSL Latency Path comes in three modes: Path 1 (Fast), Path 2 (Interleaved) and Both 1 & 2. Fast is used for applications sensitive to delay. Interleaved suits applications sensitive to errors.
PTM Priority
The PTM Proprity defines how PTM traffic packets should be handled.
| Priority | Description |
|---|---|
| Normal Priority | Send packets according to their priority. |
| High Priority | Use preemption; lower-priority packets are paused when higher-priority packets are sent. |
IP Quality of Service Algorithm
The IP Quality of Service Algorithm determines which type of QoS to provide.
Strict Priority Precedence means that where the the packets with the highest priority always are sent first.
Weighted Fair Queuing means that bandwidth is adjusted automatically according to traffic priority and weight value.
VLAN
The VLAN view allows you to configure VLAN devices.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of selectable devices.
When a particular device is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the device. |
| Base Device | Base Device to create interface for. |
| 802.1q | 802_1q tag. |
| 802.1p | 802_1q priority. |
802.1q
IEEE 802.1Q is a standard for Ethernet VLANs where VLANs are given a numeric tag. The tag is used to identify traffic in networks, and decide how to handle it.
This allows multiple bridged networks to share the same physical link without leaking information to each other networks.
802.1p
802.1p is a standard for priority levels, identifying the class of service a VLAN is to be used for. There are 8 different levels, numbered from 0 to 7.
| Priority | Acronym | Traffic types | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | BK | Background | Lowest |
| 1 | BE | Best Effort | |
| 2 | EE | Excellent Effort | |
| 3 | CA | Critical Applications | |
| 4 | VI | Video | < 100 ms latency and jitter |
| 5 | VO | Voice | < 10 ms latency and jitter |
| 6 | IC | Internetwork Control | |
| 7 | NC | Network Control | Highest |
XDSL
The xDSL view allows you to configure line settings and profiles.
The xDSL settings are divided into several tabs.
Modulation
The modulation tab lets you turn various line modulations on or off.
Configuration
| Profile | Description | Down Mbit/s | Up Mbit/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| G.Dmt | G.Dmt modulation. | 12 | 1.3 |
| G.lite | G.lite modulation. | 1.5 | 0.5 |
| T.1413 | T.1413 modulation. | 8.1 | 1.5 |
| ADSL2 | ADSL2 modulation. | 12 | 1.0 |
| AnnexL | AnnexL modulation. | 5 | 0.8 |
| ADSL2+ | ADSL2+ modulation. | 24 | 1.0 |
| AnnexM | AnnexM modulation. | 24 | 3.5 |
| VDSL2 | VDSL2 modulation. | 100 | 100 |
VDSL Profile
The VDSL Profile tab lets you turn various VDSL2 profiles on or off.
Configuration
| Profile | Bandwidth (MHz) | Downstream carriers | Carrier bandwidth (kHz) | Maximum downstream transmit power (dBm) | Max. downstream throughput (Mbit/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8a | 8.832 | 2048 | 4.3125 | +17.5 | 50 |
| 8b | 8.832 | 2048 | 4.3125 | +20.5 | 50 |
| 8c | 8.5 | 1972 | 4.3125 | +11.5 | 50 |
| 8d | 8.832 | 2048 | 4.3125 | +14.5 | 50 |
| 12a | 12 | 2783 | 4.3125 | +14.5 | 68 |
| 12b | 12 | 2783 | 4.3125 | +14.5 | 68 |
| 17a | 17.664 | 4096 | 4.3125 | +14.5 | 100 |
Capabilities
The capabilites tab lets you turn various xDSL capabilites on or off.
Configuration
| Profile | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| US0 | Upstream 0 Band. | 20 to 138 kHz |
| Bitswap | Bitswap. | Used for DMT modulation. |
| SRA | Seamless Rate Adaptation. |
Connections
The Connections view allows you configure various connection interfaces to use in your device.
View
This page allows to configure IP addresses used in your home network. In case DHCP is used, your router automatically assignes an IP address to devices connected to the network.
The page contains a list of interfaces, with one widget for each interface.
Connection Buttons
Connect
To turn a connection on:
- Select the connection you are interested in
- Click Connect button
Disconnect
To turn a connection off:
- Select the connection you are interested in
- Click Disconnect button
Edit
To change the settings for a connection:
- Select the connection you are interested in
- Click Edit button
The connection editor is shown below the connection list.
Connection Editor
You can view, manage and configure the settings for interfaces from the connections page.
Main Buttons
Delete
To change the settings for a connection:
- Select the connection you are interested in
- Click Edit button
Add
To add new connection interface:
- Select the connection you are interested in
- Click Edit button
The new interface dialog is shown.
Create Connection Wizard
The Create New Network Interface wizard allows you to create a new interface according to your needs through a number of dialogs.
Create Connection Wizard
The Create New Network Interface wizard allows you to create a new interface according to your needs through a number of dialogs.
Create Connection
The dialog is a wizard where you add information in several steps.
The number of steps and their contents varies depending on the type of interface you create.
Note: As a last step you finalize the setup, but you can further edit the settings from the connections page.
Connection Types
In the first step, you can choose the type of interface: Uplink, Downlink, or Unmanaged.
Depending on your choice in the first step, different options become available.
Uplink
An uplink interface type is an interface to services.
Interfaces
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
A Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet connection uses PPPoE to establish the network.
Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM
A Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM connection uses PPPoA to establish the network.
Point-to-point Tunnel
Dual-Stack Lite
A Dual-Stack Lite connection uses DS-Lite through an Address Family Transition Router to establish the network.
Point-to-Point Protocol over L2TP
A Point-to-Point Protocol over L2TP connection uses PPP and L2TP server to establish the network.
WWAN (LTE/HSPA+)
Overview
WWAN
A Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN), is a wireless network that extends over a large geographical distance.
HSPA / HSPA+
High Speed Packet Access (HSPA) is an extension of 3G mobile networks utilizing WCDMA.
Evolved High Speed Packet Access (HSPA+) is a furhter improvement on HSPA allowing for higher speeds.
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
DHCP v4
An DHCP v4 connection uses an IPv4 address provided by a DHCP server.
Overview
IPv4
Internet Protocol Version 4 - IPv4 - is the first major version of the Internet Protocol.
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol, adapter and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
| Ethernet Adapter | Base Device to create interface for. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
DHCP v6 (Uplink)
An DHCP v6 connection uses an IPv6 address provided by a DHCP server.
Overview
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol, adapter and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
| Ethernet Adapter | Base Device to create interface for. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
Point-to-Point Protocol
A Point-to-Point Protocol connection uses PPP to establish the network.
Overview
PPP
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a protocol for providing a direct data link connection with authentication, encryption and compression.
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
A Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet connection uses PPPoE to establish the network.
Overview
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Ethernet Adapter | Base Device to create interface for. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM
A Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM connection uses PPPoA to establish the network.
Overview
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Ethernet Adapter | Base Device to create interface for. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
3G
Overview
3G
Third-generation wireless telephone technology (3G), is a cellular network for digital mobile data communication for broadband traffic.
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
Point-to-point Tunnel
Overview
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PTPT) is a technology for virtual private networks through TCP and a GRE with PPP packets.
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
IPv6 Tunnel in IPv4
A IPv6 Tunnel in IPv4 connection uses IPv4 to transmit IPv6 traffic.
Overview
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
IPv6 Tunnel to IPv4
A IPv6 Tunnel to IPv4 connection uses IPv4 to transmit IPv6 traffic.
Overview
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
IPv6 rapid deployment
A IPv6 rapid deployment interface for IPv4 infrastructures.
Overview
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
Dual-Stack Lite
A Dual-Stack Lite connection uses DS-Lite through an Address Family Transition Router to establish the network.
Overview
DS-Lite
Dual-Stack Lite (DS-Lite) is a method for sharing of IPv4 addresses by combining IPv4-in-IPv6 and NAT.
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
Point-to-Point Protocol over L2TP
A Point-to-Point Protocol over L2TP connection uses PPP and L2TP server to establish the network.
Overview
PPP
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a protocol for providing a direct data link connection with authentication, encryption and compression.
L2TP
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a protocol used to support VPNs, where security is provided in the transmitted packages rather than in the tunneling.
Wizard
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Name | Name for the interface. |
| Interface Type | Select interface protocol type. |
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Select protocol. |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
Downlink
A Downlink interface is an interface to subscribers/clients.
Finalize
In the final step you select protocol and firewall settings for the interface.
| Item | Description | Applies to |
|---|---|---|
| Interface Type | Select interface type (Standalone / Anywan / Bridge). | |
| Physical Device | Device(s) to use for the connection. | |
| Add network to a firewall zone | Connects interface to firewall zone. |
Physical Device
For Standalone, you need to select the base device to use for the connection.
For Anywan and Bridge, you need to add a physical device to use for the connection.
| Item | Description | Applies to |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet Adapter | Selector for base device to use for the connection. | Standalone |
| Add Device | Dialog to select network device to use for the connection. | Anywan / Bridge |
Ethernet Adapter
- Select a base device from the dropdown menu.
Add Device
- Click Add
The Select Network Device dialog is shown.
- Select a network device from the dropdown menu
Unmanaged
The interface protocol type Unmanaged means that the connection has no defined protocol.
Step 1
In the first step you select basic settings for the interface.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface Type | Select interface type. |
| Add/Remove Devices | Select interface protocol type. |
- Select Interface Type
- Add as many devices as needed
Add Device
- Click Add
The Add Device dialog is shown.
- Select a network device from the dropdown menu
- Click OK
Finalize
- Click OK again
- Click Apply
Connection Editor
You can view, manage and configure the settings for interfaces from the connections page.
Edit Connections
To edit a connection:
- Click Edit button
The Connection Section is displayed at the bottom of the page.
The connection section consists of a number of tabs, showing details the connection.
Depending on connection type the tabs will be different, but the standard tabs are General, Physical Settings, and Advanced.
Additional tabs become visible as they are needed.
Default Connections
Connection Types
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
A Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet connection uses PPPoE to establish the network.
Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM
A Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM connection uses PPPoA to establish the network.
Point-to-point Tunnel
IPv6 rapid deployment
A IPv6 rapid deployment interface for IPv4 infrastructures.
Edit (ade:network:connections:6rd:start)
Dual-Stack Lite
A Dual-Stack Lite connection uses DS-Lite through an Address Family Transition Router to establish the network.
Point-to-Point Protocol over L2TP
A Point-to-Point Protocol over L2TP connection uses PPP and L2TP server to establish the network.
LAN
The default LAN connection is a DHCP v4 connection using a static IPv4 address.
Overview
IPv4
Internet Protocol Version 4 - IPv4 - is the first major version of the Internet Protocol.
Overview
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
Protocol
The protocol section contains detailed settings for the connection.
IPv4
The IPv4 section contains IP configuration.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | Device DHCP address |
| IPv4 Subnet Mask | IPv4 Subnet Mask |
| IPv4 Broadcast Mask | IPv4 Broadcast Mask |
IPv6
The IPv6 section contains IP configuration.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| IPv6 Assignment Length | Number betwen 48 and 64. |
|
| IPv6 Assigned Prefix Hint | Hexadecimal number between 1 and FFFF |
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
Configuration
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface type | The connection interface type. |
| Ethernet Adapter | Selector for base device to use for the connection. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
These DNS entries will be applied on the interface
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
Note: These custom DNS entries only affect the interface where they are added.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
DHCP
The DHCP tab allows you to enable and use a specific DHCP server for the connection.
View
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| DHCP Server | Turn DHCP Server on or off. |
| DHCP Pool Start | Start IP number for the DHCP Pool start number IP address |
| DHCP Pool Size | Number of IP addresses in the DHCP Pool |
| DHCP Lease Time | DHCP Lease Time for the LAN. |
Additional Sections
To view more details for a section, click the expand button.
Static DHCP
The Static DHCP section lets you configure IP address DHCP Leases for connected devices.
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| DHCP options | DHCP option ID:s to apply. | |
| Dynamic DHCP | Dynamically allocate client addresses. | If disabled, only configured static clients are served. |
| Force | Forces DHCP serving on the specified interface even if another DHCP server is detected on the same network segment. |
Add DHCP Option
To add DHCP option as needed:
- Click the Add option button
- Select the ID value
- Enter Option value
- Click Apply
Static DHCP
The Static DHCP section lets you configure IP address DHCP Leases for connected devices.
Configuration
| Item | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| | Add a device to the static DHCP list | |
| Device Name | Hostname for IPv4 | |
| MAC Address | Client MAC Address. | |
| IP Address | IP address for IPv4 | |
| DUID | DUID for IPv6 | |
| Host ID | Host ID for IPv6 | |
| Tag | Tag with further DHCP Options as configured in the DHCP/DNS tags settings. |
Add Static DHCP Lease
To add a static DHCP lease:
- Add an existing client or create a lease from scratch:
- To select an existing client:
- Select the desired client
- Click the
 add button
add button
- To add a static DHCP lease manually:
- Only click the
 add button
add button
The information for existing client is added automatically.
- Add or edit the client information as neeed.
- Click Save
WAN
The default WAN connection uses an IPv4 address provided by a DHCP server.
Overview
IPv4
Internet Protocol Version 4 - IPv4 - is the first major version of the Internet Protocol.
Overview
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Hostname | Hostname to use for DHCP requests. |
| Create default route | Automatically generated routing information. |
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
Configuration
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface type | The connection interface type. |
| Add/Remove Devices | Devices to associate with the connection. |
| Ethernet Adapter | Selector for base device to use for the connection. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Use broadcast flag | Add broadcast flag to traffic. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
DHCP Options
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Additional DHCP options to request from the server | DHCP option ID:s for additional options. |
| Client ID to send when requesting DHCP | Custom ID to use for DHCP requests. |
| Vendor Class to send when requesting DHCP | Use for device-specific DHCP options. |
WAN6
The default WAN6 connection is a IPv6 address provided by a DHCP server.
Overview
Overview
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Request IPv6 Address | Try / Force / None |
| Request Prefix Length | 48 / 52 / 56 / 60 / 64 / Auto / Disabled |
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
Configuration
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface type | The connection interface type. |
| Add/Remove Devices | Devices to associate with the connection. |
| Ethernet Adapter | Selector for base device to use for the connection. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
DHCP Options
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom delegated IPv6-prefix | Prefix for prefix delegation. |
| Client ID to send when requesting DHCP | Custom ID to use for DHCP requests. |
Unmanaged
An unmanaged connection has no predefined protocol for the connection.
Overview
Unmanaged
The interface protocol type Unmanaged means that the connection has no defined protocol.
Overview
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
Bridge Devices
The bridge devices section lets you add or remove bridged devices to the connection.
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
Static Address
A static address uses a fixed IP address for the connection.
Overview
Static address
A static IP address is an address that doesn't change, unless manually changed by the administrator.
Overview
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
Protocol
The protocol section contains detailed settings for the connection.
IPv4
The IPv4 section contains IP configuration.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | Device DHCP address |
| IPv4 Subnet Mask | IPv4 Subnet Mask |
| IPv4 Broadcast Mask | IPv4 Broadcast Mask |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
IPv6
The IPv6 section contains IP configuration.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| IPv6 Assignment Length | Number betwen 48 and 64. |
|
| IPv6 Assigned Prefix Hint | Hexadecimal number between 1 and FFFF |
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
Configuration
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface type | The connection interface type. |
| Ethernet Adapter | Selector for base device to use for the connection. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
DHCP
The DHCP tab allows you to enable and use a specific DHCP server for the connection.
Basic
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| DHCP Server | Turn DHCP Server on or off. |
| DHCP Pool Start | Start IP number for the DHCP Pool start number IP address |
| DHCP Pool Size | Number of IP addresses in the DHCP Pool |
| DHCP Lease Time | DHCP Lease Time for the LAN. |
| Static DHCP | Reserve an IP address DHCP Lease for a connected device. |
Advanced
IPv6
DHCP v4
An DHCP v4 connection uses an IPv4 address provided by a DHCP server.
Overview
IPv4
Internet Protocol Version 4 - IPv4 - is the first major version of the Internet Protocol.
Overview
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Hostname | Hostname to use for DHCP requests. |
| Create default route | Automatically generated routing information. |
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
Configuration
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface type | The connection interface type. |
| Add/Remove Devices | Devices to associate with the connection. |
| Ethernet Adapter | Selector for base device to use for the connection. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Use broadcast flag | Add broadcast flag to traffic. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
DHCP Options
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Additional DHCP options to request from the server | DHCP option ID:s for additional options. |
| Client ID to send when requesting DHCP | Custom ID to use for DHCP requests. |
| Vendor Class to send when requesting DHCP | Use for device-specific DHCP options. |
DHCP v6
An DHCP v6 connection uses an IPv6 address provided by a DHCP server.
Overview
Overview
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Request IPv6 Address | Try / Force / None |
| Request Prefix Length | 48 / 52 / 56 / 60 / 64 / Auto / Disabled |
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
Configuration
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface type | The connection interface type. |
| Add/Remove Devices | Devices to associate with the connection. |
| Ethernet Adapter | Selector for base device to use for the connection. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
DHCP Options
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom delegated IPv6-prefix | Prefix for prefix delegation. |
| Client ID to send when requesting DHCP | Custom ID to use for DHCP requests. |
Point-to-Point Protocol
A Point-to-Point Protocol connection uses PPP to establish the network.
Overview
PPP
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a protocol for providing a direct data link connection with authentication, encryption and compression.
Overview
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Hostname | Hostname to use for DHCP requests. |
| Create default route | Automatically generated routing information. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Enable IPv6 on the PPP link | Enables IPv6 connection from the provider. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
LCP Options
The LCP options section contains LCP configuration.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| LCP echo failure threshold | Number of echo failures before peer is considered dead. | Use 0 to ignore failures. |
| LCP echo interval | How often to send echo-requests. | Used together with failure threshold. |
| Inactivity timeout | Time until inactive connection is closed. | Use 0 to persist connection. |
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
A Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet connection uses PPPoE to establish the network.
Overview
Overview
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
Configuration
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Ethernet Adapter | Selector for base device to use for the connection. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Enable IPv6 on the PPP link | Enables IPv6 connection from the provider. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
LCP Options
The LCP options section contains LCP configuration.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| LCP echo failure threshold | Number of echo failures before peer is considered dead. | Use 0 to ignore failures. |
| LCP echo interval | How often to send echo-requests. | Used together with failure threshold. |
| Inactivity timeout | Time until inactive connection is closed. | Use 0 to persist connection. |
Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM
A Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM connection uses PPPoA to establish the network.
Overview
Overview
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Hostname | Hostname to use for DHCP requests. |
| Create default route | Automatically generated routing information. |
Physical Settings
The physical settings tab contains settings for hardware management and devices for the connection.
Configuration
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Ethernet Adapter | Selector for base device to use for the connection. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Enable IPv6 on the PPP link | Enables IPv6 connection from the provider. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
LCP Options
The LCP options section contains LCP configuration.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| LCP echo failure threshold | Number of echo failures before peer is considered dead. | Use 0 to ignore failures. |
| LCP echo interval | How often to send echo-requests. | Used together with failure threshold. |
| Inactivity timeout | Time until inactive connection is closed. | Use 0 to persist connection. |
3G
Overview
3G
Third-generation wireless telephone technology (3G), is a cellular network for digital mobile data communication for broadband traffic.
Overview
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Modem device | Modem to use for 3G traffic. |
| Service Type | Both UMTS and GPRS / Only UMTS / Only GPRS. |
| APN | Access Point Name. |
| PIN-Code | PIN code for identification. |
| PAP/CHAP Username | For authentication with PAP or CHAP. |
| PAP/CHAP Password | For authentication with PAP or CHAP. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Enable IPv6 on the PPP link | Enables IPv6 connection from the provider. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Modem Init timeout | Use DHCP DNS server. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
LCP Options
The LCP options section contains LCP configuration.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| LCP echo failure threshold | Number of echo failures before peer is considered dead. | Use 0 to ignore failures. |
| LCP echo interval | How often to send echo-requests. | Used together with failure threshold. |
| Inactivity timeout | Time until inactive connection is closed. | Use 0 to persist connection. |
WWAN (LTE/HSPA+)
Overview
WWAN
A Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN), is a wireless network that extends over a large geographical distance.
HSPA / HSPA+
High Speed Packet Access (HSPA) is an extension of 3G mobile networks utilizing WCDMA.
Evolved High Speed Packet Access (HSPA+) is a furhter improvement on HSPA allowing for higher speeds.
Overview
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Status
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device in use. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Modem device | Modem to use for WWAN traffic. |
| APN | Access Point Name. |
| PIN-Code | PIN code for identification. |
| Authentication type | PAP / CHAP / Both / None . |
| Username | For authentication with PAP or CHAP. |
| Password | For authentication with PAP or CHAP. |
| Modes | Comma-separated list of allowed network modes (all / lte / umts / gsm / cdma / td-scdma). |
| Delay | Seconds to wait before trying to interact with the modem. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
4G
Overview
4G
Fourth-generation wireless telephone technology (4G), is a cellular network for digital mobile data communication for high-speed broadband.
Overview
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Modem device | Modem to use for 4G traffic. |
| APN | Access Point Name. |
| PIN-Code | PIN code for identification. |
| PAP/CHAP Username | For authentication with PAP or CHAP. |
| PAP/CHAP Password | For authentication with PAP or CHAP. |
| Hostname to send when requesting DHCP | Hostname to include in DHCP requests. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Use broadcast flag | Add broadcast flag to traffic. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
DHCP Options
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Client ID to send when requesting DHCP | Custom ID to use for DHCP requests. | |
| Vendor Class to send when requesting DHCP | Use for device-specific DHCP options. |
Point-to-point Tunnel
Overview
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PTPT) is a technology for virtual private networks through TCP and a GRE with PPP packets.
Overview
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| VPN Server | Virtual Private Network server. |
| PAP/CHAP Username | For authentication with PAP or CHAP. |
| PAP/CHAP Password | For authentication with PAP or CHAP. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Enable IPv6 on the PPP link | Enables IPv6 connection from the provider. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
LCP Options
The LCP options section contains LCP configuration.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| LCP echo failure threshold | Number of echo failures before peer is considered dead. | Use 0 to ignore failures. |
| LCP echo interval | How often to send echo-requests. | Used together with failure threshold. |
| Inactivity timeout | Time until inactive connection is closed. | Use 0 to persist connection. |
IPv6 Tunnel in IPv4
A IPv6 Tunnel in IPv4 connection uses IPv4 to transmit IPv6 traffic.
Overview
Overview
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Local IPv4 address | IPv4 address to use instead of WAN address. |
| Remote IPv4 address | Address to use tunnel broker Point of Presence |
| Local IPv6 address | Endpoint provided by the tunnel broker. |
| IPv6 routed prefix | Prefix to be used by clients. |
| Dynamic tunnel | Dynamic update of endpoint. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use TTL on tunnnel interface | Data Time To Live. |
IPv6 Tunnel to IPv4
A IPv6 Tunnel to IPv4 connection uses IPv4 to transmit IPv6 traffic.
Overview
Overview
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Local IPv4 address | IPv4 address to use instead of WAN address. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use TTL on tunnnel interface | Data Time To Live. |
IPv6 rapid deployment
A IPv6 rapid deployment interface for IPv4 infrastructures.
Edit (ade:network:connections:6rd:start)
Overview
Overview
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| Local IPv4 address | IPv4 address to use instead of WAN address. |
| Remote IPv4 address | Address to the relay. |
| IPv6 prefix | Prefix assigned to provider. |
| IPv6 prefix length | no or 48 to 64 |
| IPv4 prefix length | Up to 43 bits. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use TTL on tunnnel interface | Data Time To Live. |
Dual-Stack Lite
A Dual-Stack Lite connection uses DS-Lite through an Address Family Transition Router to establish the network.
Overview
DS-Lite
Dual-Stack Lite (DS-Lite) is a method for sharing of IPv4 addresses by combining IPv4-in-IPv6 and NAT.
Overview
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| DS-Lite AFTR address | Address to Address Family Transition Router. |
| Local IPv6 address | IPv6 address to use instead of WAN address. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Tunnel Link | Connection to use as tunnel link. |
| Use TTL on tunnnel interface | Data Time To Live. |
Point-to-Point Protocol over L2TP
A Point-to-Point Protocol over L2TP connection uses PPP and L2TP server to establish the network.
Overview
PPP
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a protocol for providing a direct data link connection with authentication, encryption and compression.
L2TP
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a protocol used to support VPNs, where security is provided in the transmitted packages rather than in the tunneling.
Overview
General
The general tab contains status information and settings relating to the protocol.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Connection status. |
| Device | Device for the connection. |
| Protocol | Protocol in use. |
| L2TP Server | Address to Layer 2 Tunneling Protoco server. |
| PAP/CHAP Username | For authentication with PAP or CHAP. |
| PAP/CHAP Password | For authentication with PAP or CHAP. |
Advanced
The advanced tab contains settings for management of advanced features for the connection.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | Start the connection when device starts. |
| Use gateway metric | Gateway metric to use. |
| Override MAC address | Enforced MAC address to use. |
| Override MTU | MTU size to use. |
| Enable IPv6 on the PPP link | Enables IPv6 connection from the provider. |
| Use default gateway | Use default route. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | Use DHCP DNS server. |
Add/Remove custom DNS Servers
You can add as many custom DNS servers as you like, but they must be unique.
To add a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Add the IP numbers to the DNS server
- Click Save
To remove a custom DNS server:
- Click the
 delete button next to the item to delete
delete button next to the item to delete
- Click Save
Routes
Static routes are useful if you have several networks accessible from your router and you want to correctly route packets between them.
Overview
Add Static Route
To add a static route:
- Click the add button
- Enter information for the route fields.
- Click Apply
IPv4 Routes
The IPv4 section lets you add static routes for IPv4 .
Configuration
| Item | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Affected connection for the route. | |
| Target | Destination IP address. | |
| Netmask | Applicable netmask. | |
| Gateway | IP address to the internet gateway. | |
| Metric | Route metric. | |
| MTU | MTU size to use. | |
| Delete | Remove route. |
IPv6 Routes
The IPv6 section lets you add static routes for IPv6 .
Configuration
| Item | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Affected connection for the route. | |
| Target | Destination IP address. | |
| Gateway | IP address to the internet gateway. | |
| Metric | Route metric. | |
| MTU | MTU size to use. | |
| Delete | Remove route. |
Firewall
The firewall lets you filter traffic, set up port forwarding or expose particular services to the outside world.
Overview
Forwarding
Port Forwarding allows remote computers to connect to a specific device within your private network.
DMZ / Exposed Host
A local network device can be made an Exposed Host. It is placed in the DMZ outside of the firewall, which provides unrestricted Internet access to the network device.
General Settings
The general settings view allows you to turn the firewall on or off.
Firewall Settings
To enable the firewall:
- Click Enable Firewall
Zones
The Zones view lets you can configure firewall zones to group your firewall rules.
At the top of the page is a list of selectable zones.
By default this list contains the LAN and WAN zones, which contain default settings for local and Internet traffic.
When a particular interface is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
Zone configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Identifier for the zone. |
| Default policy | Default behavior for various traffic. |
| Masquerading | Enable firewall masquerading. |
| MSS Clamping | MSS Clamping limit. |
| Allow forward to destination zones | Check zones to permit forwarding. |
| Allow forward from source zones | Check zones to permit forwarding. |
| Zone members | Interfaces that are part of the zone. |
Default Policy
The default policy setting defines firewall rules that apply unless specific rules override them.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Input | Incoming traffic from WAN. |
| Output | Outgoing traffic to WAN. |
| Forward | Traffic from LAN to WAN. |
The different default policy values determine the firewall behavior, through the firewall actions:
Firewall Action
The firewall action defines how traffic is handled by the firewall.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| ACCEPT | Allow the traffic. |
| REJECT | Refuse the traffic. |
| DROP | Ignore the traffic. |
| FORWARD | Pass the traffic along. |
Add Firewall Zone
To add a firewall zone:
- Click the Add button
- Enter information in the fields
- Click Apply
Once the zone has been created, you can use it with your connections.
Add Zone Members
If you have networks/devices set up, you can add them to the zone.
To add a device as a zone member:
- Click the Add button
The Select network device dialog opens.
- Open the select network menu
- Select the device
- Click OK
- Click Apply
Rules
Firewall rules are more fine grained filtering rules for filtering your traffic.
View
The page shows the configured rules. Each rule can be modified by clicking the Edit button.
Once you have chosen to edit one rule, the edit view is shown consistently, and you can quickly switch between configured rules by selecting them in the list.
Configuration
When a particular interface is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
General
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn firewall rule on or off. | |
| Expose To | Users with access to the rule. | |
| Name | Identifier for the rule. |
Source / Destination
Where applicable, the configuration is divided into separate sections for source and destination zones.
Parameters
Add Firewall Rule
- Click the Add button
A new rule named new_rule is added at the bottom of the list.
- Click the Edit button for the new rule
- Enter properties as needed.
- Click OK
- Click Apply
Reorder Firewall Rules
The firewall rules are applied in order from top to bottom in the list.
You can rearrange the rules by using the buttons:
| | Move up | |
| | Move down |
Default Firewall Rules
A number of sample firewall rules are enabled by default, providing a basic set of filtering for the network.
| Rule | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Allow-Ping | Permit ping from WAN to device. |
| Allow-DHCP-Renew | Permit traffic from WAN to any zone. |
| Allow-IGMP | Permit IGMP traffic from WAN to IPv4 devices. |
| Allow-DHCPv6 | Permit IPV6 traffic from WAN to IPV6 device. |
| Allow-MLD | Permit MLD traffic over ICMP from WAN to IPV6 devices. |
| Allow-ICMPv6-Input | Permit ICMP traffic from WAN to IPV6 devices. |
| Allow-ICMPv6-Forward | Permit ICMP traffic from WAN to any zone. |
| Allow-IPsec/ESP | Permit IPsec over ESP traffic from WAN to LAN. |
| Allow-ISAKMP-Passthrough | Permit ISAKMP over UDP traffic from WAN to LAN. |
Forwarding
Port Forwarding allows remote computers to connect to a specific device within your private network.
Configuration
The forwarding list shows information about any configured port forwarding rules.
Overview
Add or Edit Port Mapping
The Add or Edit Port Mapping view allows you to add or change port mapping settings.
Add or Edit Port Mapping
The Add or Edit Port Mapping view allows you to add or change port mapping settings.
Configuration
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Rule Name | Rule name. | |
| Source Zone | Incoming zone. | |
| Destination Zone | Destination zone. | |
| Source IP Address | Source IP address (for filtering). | |
| Dst. Device | Client hostname. | |
| Dst. IP Address | Client IP address. | |
| Protocol | Mapping protocol | (UDP / TCP / TCP + UDP ). |
| Public port(s) | Public (external) port. | |
| Private port(s) | Private (client) port. | |
| NAT Loopback | Enable NAT Loopback |
Protocol
The protocol setting filters traffic by protocol for the port forward.
Port Mapping Settings
To map incoming connections:
- Click the
 add button to open the settings
add button to open the settings
The port mapping dialog lets you add configuration settings for the mapping.
Ports can be added one by one (80) or as ranges (21:22).
- Add information:
- Add a name as identification
- Add ports:
- Add public/incoming port(s)
- Add private/client port(s)
- Select protocol
- Click Save
- Click Close
Your information is saved and is visible in the mapping list.
DMZ / Exposed Host
A local network device can be made an Exposed Host. It is placed in the DMZ outside of the firewall, which provides unrestricted Internet access to the network device.
Configuration
| WAN IP Address | Public IPv4 and IPv6 address for the DMZ. |
| Host IPv4 Address | IPv4 of device to place in DMZ. |
| Host IPv6 Address | IPv6 of device to place in DMZ. |
| Select Existing Host | Dropmenu to select connected devices. |
Add Exposed Host
To allow DMZ/exposed host:
- Click Enable to enable an exposed host
- Enter the local IP address to expose
- Alternatively, click select existing host
Note: You should also configure the DMZ IP address as static DHCP address for your device.
Parental Control
Parental control is used to restrict access to the network for particular devices.
Internet Access Scheduling
Parental control is handled by setting schedules where access is restricted to explicitly named MAC addresses.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Weekdays | List of days the filter applies. |
| Start Time | Time of day to start filtering. |
| Stop Time | Time of day to stop filtering. |
| Host Names | List of devices / MAC addresses. |
Overview
Add / Edit MAC Filter Scheduling
The Add / Edit MAC Filter Scheduling view allows you to add or change parental control rules.
Add / Edit MAC Filter Scheduling
The Add / Edit MAC Filter Scheduling view allows you to add or change parental control rules.
Configuration
| Item | Comment | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Time Frame | Quick select for time predefined time periods. | Individual Days/Every Day/Every Workday/All Weekend |
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Weekdays | List of days the filter applies. |
| Start Time | Time of day to start filtering. |
| Stop Time | Time of day to stop filtering. |
| Mac List | Dropdown to select list of devices / MAC addresses to include in the rule. |
Start and Stop Times
The start time for a rule has to be lower than the end time.
If you want to have a rule that goes over midnight, you need to add two rules, one up until midnight, and one from midnight to when you want the rule to end.
For example:
Rule one: From 21:00 To 23:59
Rule two: From 00:00 To 06:00
A single rule of From 21:00 To 06:00 will not be saved.
Quality Of Service
The Quality Of Service view allows you to configure parameters for Quality of Service through applying groups of classes to interfaces.
Interface views
Interface
The interface tab lets you select interfaces and configure Quality of Service profiles for them.
Classification Group
The Classification Group tab lets you manage groupings of QoS classes.
classgroup blocks are used to define different class groupings. This is only really useful if you wish to have multiple interfaces with different class considerations, for example, you might want eth1 to have an ultrapriority class or something.
This is useful when you have multiple interfaces and want to manage classes differently for them.
Classify
Reclassify
The Reclassify tab lets you configure filtering parameters in order to redefine types of traffic to include in which Class.
Reclassification can override the class on a per packet basis without altering the defined classification .
Workflow
Workflow
In order to use Quality of Service on the traffic for your device, you need to perform a number of configurations.
1: Class
The classes define how network traffic is to be prioritized and allocated.
There are a number of predefined classes, but you can add your own.
2: Classify/Reclassify
In order to direct traffic to the correct classes, you need to define classificaton rules in the Classify tab.
Since the classification only affects connections that haven't already been classified you may also need to apply filters in the Reclassify tab.
3: Class Group
With the classes defined, you can add and order them in a class group in the Class Group tab.
If you have multiple interfaces, and want different QoS settings for them, you can create multiple class groups.
Workflow
In order to use Quality of Service on the traffic for your device, you need to perform a number of configurations.
Process
Configuration steps
The order of operations involved in configuring QoS is different from the order in which the interface displays the setting tabs. Not all settings are needed in all cases.
1: Class
The classes define how network traffic is to be prioritized and allocated.
There are a number of predefined classes, but you can add your own.
2: Classify/Reclassify
In order to direct traffic to the correct classes, you need to define classificaton rules in the Classify tab.
Since the classification only affects connections that haven't already been classified you may also need to apply filters in the Reclassify tab.
3: Class Group
With the classes defined, you can add and order them in a class group in the Class Group tab.
If you have multiple interfaces, and want different QoS settings for them, you can create multiple class groups.
1: Class
The classes define how network traffic is to be prioritized and allocated.
There are a number of predefined classes, but you can add your own.
Predefined Classes
Class
There are a number of predefined classes QoS classes. Each class is a set of definitions for a token bucket.
Default Settings
The predefined classes can be edited and all values changed, but they have default settings that should be suitable in normal cases.
Priority
The priority class is an upstream class for high priority traffic such as handshaking and ICMP packets.
Priority_down
The Priority_down class is an downstream class for high priority traffic.
Express
The Express class is for interactive applications that require bandwidth above standard services so that interactive apps run smoothly.
Normal
The Normal Class is the standard upstream class for all services.
This class will apply to all services not otherwise defined.
Normal_down
The Normal_down class is the standard downstream class for all services.
This class will apply to all services not otherwise defined.
Bulk
The bulk class is suitable for very low priority traffic. It will be allocated available bandwidth if other classes are idle. When other classes are active, it will be allocated bandwidth according to the priority setting.
It is suitable for transfer services such as (P2P and FTP).
Tab
Class
The class tab lets you manage QoS classes.
Overview
At the top of the page is a list of selectable classes.
When a particular class is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Priority | Bandwidth allocation limit (%). | |
| Average Rate | Average target rate (%). | |
| Limit Rate | Maximum allowed bandwidth (%). | |
| Packet Size | Size of packets (bytes). | See note. |
| Packet Delay | Target delay for packets (ms). | See note. |
| Max Size | Maximum size of packets (bytes). |
Note: Packet Size and Packet Delay rely on the Average Rate setting. The average rate is impacted by the maximum packet delay and the transfer time for the packet size. Generally the delay is lower for smaller packet sizes.
Configuration Values
Priority
The Priority indicates the bandwidth allocation limit as a percentage of total available bandwidth.
ls m2 = priority / sum (priority) * max_bandwidth
Limit Rate
The Limit Rate provides a maximum allowed bandwidth, expressed as a percentage of the total available bandwidth.
ul rate = limitrate * max_bandwidth / 100
Average Rate
The Average target rate is a percentage of the total available bandwidth.
Average rate for this class, value in % of bandwidth (this value uses for calculate vaues
'Nx' of 'tc … hfsc rt m1 N1 d N2 m2 N3'
Note: Packet Size and Packet Delay rely on the Average Rate setting. The average rate is impacted by the maximum packet delay and the transfer time for the packet size. Generally the delay is lower for smaller packet sizes.
Packet Size
Size of packets (bytes).
packetsize & packetdelay: (only works if avgrate is present)
rt d = max( packetdelay, 'time required for packetsize to transfer') ls d = rt d
Packet Delay
Target delay for packets (ms).
Max Size
The maximum size of packets indicates the maximum packet size in iptables.
2: Classify/Reclassify
In order to direct traffic to the correct classes, you need to define classificaton rules in the Classify tab.
Since the classification only affects connections that haven't already been classified you may also need to apply filters in the Reclassify tab.
Tabs
Classify
The classify tab lets you configure filtering parameters in order to define types of traffic to include in which Class.
Classification assigns a class to traffic in a connection, but only affect connections which have not been assigned a traffic class already.
Overview
At the top of the page is a list of selectable classification groups.
When a particular group is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
Adding a parameter will filter out traffic according to the parameters and assign it to the group.
| Item | Description | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Classification Group to assign. | As configured in classification group settings | |
| Protocol | Protocol affected. | All / UDP / TCP / ICMP | |
| Source Host | Originating host(s) to affect. | All / Specific host | |
| Destination Host | Receiving host(s) to affect. | All / Specific host | |
| Ports | Settings for ports filtering. | Port/Source/Destination/Port range | |
| Direction | Direction of traffic to be affected by the classificaton. | Both/In/Out | |
| Connbytes | Connection Bytes for when to start filtering. |
Ports Filtering
Reclassify
The Reclassify tab lets you configure filtering parameters in order to redefine types of traffic to include in which Class.
Reclassification can override the class on a per packet basis without altering the defined classification .
Overview
At the top of the page is a list of selectable classification groups.
When a particular group is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
Adding a parameter will filter out traffic according to the parameters and assign it to the group.
| Item | Description | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Classification Group to assign. | As configured in classification group settings | |
| Protocol | Protocol affected. | All / UDP / TCP / ICMP | |
| Source Host | Originating host(s) to affect. | All / Specific host | |
| Destination Host | Receiving host(s) to affect. | All / Specific host | |
| Ports | Settings for ports filtering. | Port/Source/Destination/Port range | |
| Direction | Direction of traffic to be affected by the classificaton. | Both/In/Out | |
| Connbytes | Connection Bytes for when to start filtering. | ||
| Precedence | Quality of service parameters relating for precedence. | ||
| Packet Size | Size of packets to match. | Minimum size From or From-To range. | |
| Mark | Hexadecimal mark code to att to the packets. (0x000000-0xFFFFFF) | ||
| TCP flags | TCP Flags to match. | SYN/ACK/FIN/RST/URG/PSH |
Ports Filtering
3: Class Group
With the classes defined, you can add and order them in a class group in the Class Group tab.
If you have multiple interfaces, and want different QoS settings for them, you can create multiple class groups.
Tab
Classification Group
The Classification Group tab lets you manage groupings of QoS classes.
classgroup blocks are used to define different class groupings. This is only really useful if you wish to have multiple interfaces with different class considerations, for example, you might want eth1 to have an ultrapriority class or something.
This is useful when you have multiple interfaces and want to manage classes differently for them.
Overview
At the top of the page is a list of selectable classification groups.
When a particular group is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Default Class | Class to use as fallback if packets don't match any other class. | |
| Classes | Classes to include in the group. | Note: You need to create a class for it to be available in the list. |
The Default Classgroup contains these standard classes: - Priority - Express - Normal - Bulk
4: Enable
As a final step, you enable QoS for the desired interface in the Interface tab.
Tab
Interface
The interface tab lets you select interfaces and configure Quality of Service profiles for them.
Overview
At the top of the page is a list of selectable interfaces.
When a particular interface is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable QoS | Turn the Quality of Service on for the interface. | ||
| Classification Group | Classification group to use for the interface. | Note: You need to create the group for it to be available in the list. | |
| Calculate Overhead | Include overhead in the packet calculations for shaping and policing. | ||
| Limit Download Speed | Restrict the network speed to clients. | ||
| Limit Upload Speed | Restrict the network speed from clients. |
Class
The class tab lets you manage QoS classes.
Overview
At the top of the page is a list of selectable classes.
When a particular class is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Priority | Bandwidth allocation limit (%). | |
| Average Rate | Average target rate (%). | |
| Limit Rate | Maximum allowed bandwidth (%). | |
| Packet Size | Size of packets (bytes). | See note. |
| Packet Delay | Target delay for packets (ms). | See note. |
| Max Size | Maximum size of packets (bytes). |
Note: Packet Size and Packet Delay rely on the Average Rate setting. The average rate is impacted by the maximum packet delay and the transfer time for the packet size. Generally the delay is lower for smaller packet sizes.
Add Class
You can add as many classes as you like.
Add Class
To add a class:
- Click the Add button
- Enter a Name for the class
- Enter QoS values as needed.
- Click Apply
Class
There are a number of predefined classes QoS classes. Each class is a set of definitions for a token bucket.
Default Settings
The predefined classes can be edited and all values changed, but they have default settings that should be suitable in normal cases.
Priority
The priority class is an upstream class for high priority traffic such as handshaking and ICMP packets.
Priority_down
The Priority_down class is an downstream class for high priority traffic.
Express
The Express class is for interactive applications that require bandwidth above standard services so that interactive apps run smoothly.
Normal
The Normal Class is the standard upstream class for all services.
This class will apply to all services not otherwise defined.
Normal_down
The Normal_down class is the standard downstream class for all services.
This class will apply to all services not otherwise defined.
Bulk
The bulk class is suitable for very low priority traffic. It will be allocated available bandwidth if other classes are idle. When other classes are active, it will be allocated bandwidth according to the priority setting.
It is suitable for transfer services such as (P2P and FTP).
Interface
The interface tab lets you select interfaces and configure Quality of Service profiles for them.
Overview
At the top of the page is a list of selectable interfaces.
When a particular interface is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable QoS | Turn the Quality of Service on for the interface. | ||
| Classification Group | Classification group to use for the interface. | Note: You need to create the group for it to be available in the list. | |
| Calculate Overhead | Include overhead in the packet calculations for shaping and policing. | ||
| Limit Download Speed | Restrict the network speed to clients. | ||
| Limit Upload Speed | Restrict the network speed from clients. |
Add Interface
You can add Interfaces as needed.
Add Interface
To add an interface:
- Click the Add button
The interface dialog opens.
- Select an Interface from the list
- Click OK
- Enable other settings as needed:
- Turn QoS on with the Enable QoS slider
- Select an available Classification Group
- Turn QoS on with the Limit Download Speed slider
- Enter a speed value (kbps)
- Turn QoS on with the Limit Upload Speed slider
- Enter a speed value (kbps)
- Click Apply
Classification Group
The Classification Group tab lets you manage groupings of QoS classes.
classgroup blocks are used to define different class groupings. This is only really useful if you wish to have multiple interfaces with different class considerations, for example, you might want eth1 to have an ultrapriority class or something.
This is useful when you have multiple interfaces and want to manage classes differently for them.
Overview
At the top of the page is a list of selectable classification groups.
When a particular group is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Default Class | Class to use as fallback if packets don't match any other class. | |
| Classes | Classes to include in the group. | Note: You need to create a class for it to be available in the list. |
The Default Classgroup contains these standard classes: - Priority - Express - Normal - Bulk
Add Classification Group
You can add Classification Groups as needed.
Add Classification Group
To add a class group:
- Click the Add button
- Enter a Name for the group
- Select Default group
- Add classes as needed:
- Click Add a new class
- Select the desired class from the list
- Click Apply
Classify
The classify tab lets you configure filtering parameters in order to define types of traffic to include in which Class.
Classification assigns a class to traffic in a connection, but only affect connections which have not been assigned a traffic class already.
Overview
At the top of the page is a list of selectable classification groups.
When a particular group is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
Adding a parameter will filter out traffic according to the parameters and assign it to the group.
| Item | Description | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Classification Group to assign. | As configured in classification group settings | |
| Protocol | Protocol affected. | All / UDP / TCP / ICMP | |
| Source Host | Originating host(s) to affect. | All / Specific host | |
| Destination Host | Receiving host(s) to affect. | All / Specific host | |
| Ports | Settings for ports filtering. | Port/Source/Destination/Port range | |
| Direction | Direction of traffic to be affected by the classificaton. | Both/In/Out | |
| Connbytes | Connection Bytes for when to start filtering. |
Ports Filtering
Add Classification Group
You can add Classification Filters as needed.
Add Filter
To add a filter:
- Click the Add button
- Select Classification group
- Enter QoS values as needed.
- Click Apply
Order
The filters are prioritized in order from top to bottom in the list.
Reorder
You can rearrange the classes by using the buttons:
| | Move up | |
| | Move down |
Reclassify
The Reclassify tab lets you configure filtering parameters in order to redefine types of traffic to include in which Class.
Reclassification can override the class on a per packet basis without altering the defined classification .
Overview
At the top of the page is a list of selectable classification groups.
When a particular group is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
Adding a parameter will filter out traffic according to the parameters and assign it to the group.
| Item | Description | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Classification Group to assign. | As configured in classification group settings | |
| Protocol | Protocol affected. | All / UDP / TCP / ICMP | |
| Source Host | Originating host(s) to affect. | All / Specific host | |
| Destination Host | Receiving host(s) to affect. | All / Specific host | |
| Ports | Settings for ports filtering. | Port/Source/Destination/Port range | |
| Direction | Direction of traffic to be affected by the classificaton. | Both/In/Out | |
| Connbytes | Connection Bytes for when to start filtering. | ||
| Precedence | Quality of service parameters relating for precedence. | ||
| Packet Size | Size of packets to match. | Minimum size From or From-To range. | |
| Mark | Hexadecimal mark code to att to the packets. (0x000000-0xFFFFFF) | ||
| TCP flags | TCP Flags to match. | SYN/ACK/FIN/RST/URG/PSH |
Ports Filtering
Order
The filters are prioritized in order from top to bottom in the list.
Reorder
You can rearrange the classes by using the buttons:
| | Move up | |
| | Move down |
Add Filter
You can add Reclasssify filters as needed.
Add Filter
To add a filter:
- Click the Add button
- Select Classification group
- Enter QoS values as needed.
- Click Apply
Add WAN
MultiWAN
The MultiWAN view allows you to create and configure WAN traffic divisions for load balancing and failover and applying traffic rules.
Introduction
Using the MultiWAN feature, you can enable up to 250 WAN interfaces to:
- Provide load balancing over multiple WAN interfaces based on a numeric weight assignment.
- Monitor connections using repeated ping tests and can automatically route outbound traffic to another WAN interface if the first WAN interface loses connectivity.
- Set rules to customize which outbound connections should use which WAN interface
- Customize rules based on various parameters such as IP:s, port(s) and protocol.
Why should I use mwan3?
If you have multiple internet connections, you want to control which traffic goes through which WANs
Mwan3 can handle multiple levels of primary and backup interfaces, load-balanced or not. Different sources can have different primary or backup WANs.
Mwan3 uses netfilter mark mask to be compatible with other packages (such as OpenVPN, PPTP VPN, QoS-script, Tunnels, etc) as you can configure traffic to use the default routing table.
Mwan3 can also load-balance traffic originating from the router itself
Tabs
The MultiWAN settings are divided into tabs.
Settings
The MultiWAN Settings tab allows you to add or edit multiple WAN connections and turn them on or off. You can also configure thresholds for WAN up/down detection and reliability monitoring.
Members
The Members tab allows you to create member groups for interfaces, to use with policies for traffic management. The metric and weight settings are used to manage traffic in the member groups.
Policies
The Policies tab allows you to group members into policy sets for use with the traffic rules.
Rules
The Rules tab allows you to define how LAN traffic should be filtered and distributed over the available WANs.
Rules are the way the Policies are applied to the traffic. Each Rule targets packets with some kind of filter.
The Rules are applied in order from top to bottom. Multiple rules that can use the same policy but target different traffic.
Workflow
1: WAN Interfaces
As a first step, you need to add all network interfaces that should be part of the MultiWAN.
2: Members
Next, each interface must have at least one member, with per interface giving it appropriate Metric and Weight.
3: Policies
With the members set up, you must create at least one policy containing at least two members.
Workflow
In order to use the multiwan feature, you need to do a number of configurations.
Process
Configuration Steps
The order of operations involved in configuring MultiWan is roughly the same as the order in which the interface displays the setting tabs.
1: WAN Interfaces
As a first step, you need to add all network interfaces that should be part of the MultiWAN.
2: Members
Next, each interface must have at least one member, with per interface giving it appropriate Metric and Weight.
3: Policies
With the members set up, you must create at least one policy containing at least two members.
1: WAN Interfaces
As a first step, you need to add all network interfaces that should be part of the MultiWAN.
Important
The following prerequisites apply:
- The interface must be enabled and working.
- All addresses defined in the Host(s) to ping settings are reachable from the interface.
- The Create Default Route must be enabled for the interface.
- The Gateway Metric must be unique for the interface.
Tab
Settings
The MultiWAN Settings tab allows you to add or edit multiple WAN connections and turn them on or off. You can also configure thresholds for WAN up/down detection and reliability monitoring.
Configuration
Below the general settings is a list of selectable WANs.
When a particular WAN is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn WAN on or off. | |
| Family | Type of WAN. | IPv4 / IPv6 |
| Tracking Type | Method to determine if the WAN is online. | IP / Gateway / DNS |
| Host(s) to ping | List of hosts to ping. | Used to determine WAN status. If this value is not set, the interface is always considered up. |
| Interface Reliability | Number of hosts that must reply for the interface to be considered up. | At least this many hosts must be defined or the interface will always be considered down. |
| Number of Pings | Number of pings to send to each host. | |
| Timeout | Number of seconds to wait for reply from host. | |
| Interval | Number of seconds between each test. | |
| Up | Number of successful tests to consider interface as up. | |
| Down | Number of failed tests to consider interface as down. |
Overview
2: Members
Next, each interface must have at least one member, with per interface giving it appropriate Metric and Weight.
Naming The Members
A good way to keep track of the members and make them easier to find when applying policies, is to use a regular naming scheme.
The following scheme will provide a good structure:
<interface>_m<metric>_w<weight>
and allow you to know the setup from the name alone.
Tabs
Members
The Members tab allows you to create member groups for interfaces, to use with policies for traffic management. The metric and weight settings are used to manage traffic in the member groups.
Configuration
Below the general settings is a list of selectable members.
When a particular member is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Interface configured in the settings tab. | |
| Metric | Precedence metric. | Members within one policy with a lower metric have precedence over higher metric members. |
| Weight | Distribution weight. | Members with same metric will distribute load based on this weight value. |
3: Policies
With the members set up, you must create at least one policy containing at least two members.
Tab
Policies
The Policies tab allows you to group members into policy sets for use with the traffic rules.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of policies.
When a particular policy is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Selected members | List of members configured in the members tab. |
4: Rules
As the final step you can set up the rules that will govern how traffic is handled.
Tab
Rules
The Rules tab allows you to define how LAN traffic should be filtered and distributed over the available WANs.
Rules are the way the Policies are applied to the traffic. Each Rule targets packets with some kind of filter.
The Rules are applied in order from top to bottom. Multiple rules that can use the same policy but target different traffic.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of rules.
When a particular rule is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Policy to use | Policy configured in the policies tab. | Default means the default routing table will be used. |
| Any Source IP | Enable to match all origins, regardless of IP address. | |
| Source Address | External target IP address. | |
| Source Port | Range of ports to match. | |
| Any Destination IP | Enable to match all destinations, regardless of IP address. | |
| Destination Address | External target IP address. | |
| Destination Port | Range of ports to match. | |
| Protocol | Protocols affected by the rule. | All / TCP / UDP / ICMP |
Members is a way to define multiple ways to prioritize the Interfaces that Multiwan is using. The prioritizing is done using Metric and Weight. The Member within one policy with a lower metric have precedence over higher metric members. Members within one policy with the same metric will distribute load based on this weight value (Example weight 1 and 4 will balance the traffic so the first interface gets 20% of traffic and the second gets 80%.
Policies is just a way to hold 1 or more members.
It is NOT possible to add multiple members from the same interface if they have the same metric (if the metric are different it doesn’t make sense to add multiple members from the same interface because the one with the lowest will always be used but its allowed).
Rules are the way the Policies are applied to the traffic. Each Rule targets packets with some kind of filter. The Rules are applied in order from top to bottom, this means that there can be multiple rules that is using same or different policy that targets different traffic.
- Create all the interface sections needed each corresponding to one of the network interfaces that should be tracked by Multiwan.
Make sure that the Host(s) to ping are reachable from the interface when the interface is working correctly and that the interface is Enabled! All network interfaces used in Multiwan must work by them self and all of them need to have a default route, this is only possible if the interfaces have different metric set in the network configuration.
- Create at least one member per interface giving it appropriate Metric and Weight.
A good naming practice is to name the Members <interface>m<metric>w<weight>, this way they will be easy to add to the Policies.
- Create at least one Policy containing at least two members each.
- Set up the rules to the specifications. Example: some traffic might only be relevant on one interface when other traffic can be ether balanced or used in a fallback scenario (One interface as default and a fallback if the default goes down).
Settings
The MultiWAN Settings tab allows you to add or edit multiple WAN connections and turn them on or off. You can also configure thresholds for WAN up/down detection and reliability monitoring.
Configuration
Below the general settings is a list of selectable WANs.
When a particular WAN is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn WAN on or off. | |
| Family | Type of WAN. | IPv4 / IPv6 |
| Tracking Type | Method to determine if the WAN is online. | IP / Gateway / DNS |
| Host(s) to ping | List of hosts to ping. | Used to determine WAN status. If this value is not set, the interface is always considered up. |
| Interface Reliability | Number of hosts that must reply for the interface to be considered up. | At least this many hosts must be defined or the interface will always be considered down. |
| Number of Pings | Number of pings to send to each host. | |
| Timeout | Number of seconds to wait for reply from host. | |
| Interval | Number of seconds between each test. | |
| Up | Number of successful tests to consider interface as up. | |
| Down | Number of failed tests to consider interface as down. |
Overview
Add WAN
You can add as many WANS as you have WAN interfaces.
Add WAN Interface
To add a WAN:
- Click the Add button
- Select an available Interface
A new WAN is added to the list.
- Edit the parameters as needed.
- Click Apply
Members
The Members tab allows you to create member groups for interfaces, to use with policies for traffic management. The metric and weight settings are used to manage traffic in the member groups.
Configuration
Below the general settings is a list of selectable members.
When a particular member is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Interface configured in the settings tab. | |
| Metric | Precedence metric. | Members within one policy with a lower metric have precedence over higher metric members. |
| Weight | Distribution weight. | Members with same metric will distribute load based on this weight value. |
Add Member
You can add as many rules as you like.
Add Member
To add a member:
- Click the Add button
- Enter a Name
A new rule is added to the list.
- Select the WAN to add as member
- Edit the parameters as needed.
- Click Apply
Policies
The Policies tab allows you to group members into policy sets for use with the traffic rules.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of policies.
When a particular policy is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Selected members | List of members configured in the members tab. |
Add Policy
You can add as many Policies as you like.
Add Policy Configuration
To add a policy:
- Click the Add button
- Enter a Name
A new member is added to the list.
- Click the Edit button
- Select members to add to the policy
- Click Apply
Rules
The Rules tab allows you to define how LAN traffic should be filtered and distributed over the available WANs.
Rules are the way the Policies are applied to the traffic. Each Rule targets packets with some kind of filter.
The Rules are applied in order from top to bottom. Multiple rules that can use the same policy but target different traffic.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of rules.
When a particular rule is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Policy to use | Policy configured in the policies tab. | Default means the default routing table will be used. |
| Any Source IP | Enable to match all origins, regardless of IP address. | |
| Source Address | External target IP address. | |
| Source Port | Range of ports to match. | |
| Any Destination IP | Enable to match all destinations, regardless of IP address. | |
| Destination Address | External target IP address. | |
| Destination Port | Range of ports to match. | |
| Protocol | Protocols affected by the rule. | All / TCP / UDP / ICMP |
Add Rule
You can add as many rules as you like.
Add Rule
To add a rule:
- Click the Add button
- Enter a Name (Note: This cannot be changed later.)
A new rule is added to the list.
- Click the Edit button
- Edit the parameters as needed.
- Click Apply
Services
The Services view allows you to configure the services connected device.
Overview
Printer Server
The Printer Server Settings view allows you to change different features about your printer server for connected printers.
Printer Server
The Printer Server Settings view allows you to change different features about your printer server for connected printers.
Configuration
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| Enable | Turn printer server on or off. |
| Interface | Interface to listen on |
| Port | Port to listen on. |
| Bidirectional mode | Allow printer to communicate with client. |
MiniDLNA
The MiniDLNA view lets you configure the MiniDLNA server.
Overview
Status
For Enabled At the top of the page is a status window that can be expanded to display the current MiniDLNA status.
General
In the General settings tab you can change different general features about your MiniDLNA server.
Status
For Enabled At the top of the page is a status window that can be expanded to display the current MiniDLNA status.
Show Status
To view the status window, click the expand icon.
Media Library
In the media library table, the number of audio, video and image files on the server is shown.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Audio files | 0 |
| Video files | 0 |
| Image files | 0 |
Connected Clients
The Connected Clients table displays information about possible clients and their connections to the server.
General
In the General settings tab you can change different general features about your MiniDLNA server.
Configuration
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| Port | Port for HTTP traffic. |
| Network | List of interfaces to serve. |
| Friendly Name | Name to display to clients. |
| Root Container | Start point when browsing. |
| Media Directories | File system locations for media. |
| Album-Art Names | List of file names for album art. |
Advanced
In the Advanced tab you can change different advanced features about your media server.
Configuration
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| Database directory | Directory for database and cache storage. |
| Log directory | Directory to store logs. |
| Enable inotify | Turn Inotify on or off. |
| Enable TIVO | Support for streaming files to TiVo. |
| Strict to DLNA standard | Only use DLNA standard features. |
| Presentation URL | Default presentation URL. |
| Notify interval | Time between notification messages. |
| Announced serial number | Serial number to show to clients. |
| Announced model number | Model number to report to clients. |
| miniSSDP socket | Path to miniSSDPd socket for SSDP. |
UPnP
The UPNP view allows you to configure UPNP services.
At the top of the page is a list of currently open UPnP ports, if any.
The UPnP settings are divided into tabs.
General
The General tab allows you to enable and configure the service parameters.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable UPNP | Enable UPNP protocol |
| Enable NAT-PMP | Enable NAT-PMP protocol. |
| Enable secure mode | Only add forwards to requesting ip addresses. |
| Enable additional logging | Add extra debugging information to the system log. |
| Downlink | Nominal uplink speed (KByte/s). |
| Uplink | Nominal downlink speed (KByte/s). |
| Port | Port for the service. |
| External Interface | Interface for external access. |
| Internal Interface | Interface to use for local access. |
Advanced
The Advanced tab lets you configure advanced UPNP settings.
Configuration
| Device UUID | UUID |
| Announced serial number | Serial number to show to clients. |
| Announced model number | Model number to show to clients. |
| Notify interval | Time between notification messages. |
| Clean rules threshold | Number of rules to keep. |
| Clean rules interval | Time between cleaning of UPnP rules. |
| Presentation URL | Location for service control web interface. |
| UPnP lease file | Location for file containing leases. |
DDNS
The DDNS view allows you configure Dynamic DNS services for your device.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of selectable services.
When a particular service is selected, details about it is shown in the connection section.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn service on or off. |
| Label | Identifier in the service list. |
| IP Retrieval Method | Interface / Network / Script / Web. |
| Select Interface | For Interface: Interface. |
| Select Connection | For Network: Connection. |
| Script Path | For Script: Local path to IP detection script. |
| Enter website to poll for ip address | For Web: Address to IP detection service. |
| Provider | Service provider list. |
| Enter DDNS Provider | Manually add service provider. |
| Domain name | Full hostname to use for the device. |
| Username | Service account username. |
| Password | Service account password. |
| Use HTTPS | USe secure communication with service. |
DDNS Services
You can add as many DDNS Services as you like.
To add a DDNS Service:
- Click the add button
A new service is added to the list.
- Edit the parameters as needed.
- Click Apply
IPTV
The IPTV view lets you configure the IPTV server.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Differentiated Services Code Point | DSCP to use for tagging outgoing IGMP packets. |
| Proxy interface | Interface to use as proxy. |
| Default version | IGMP version. |
| Query interval | Time between IGMP query messages. |
| Query response interval | Time to wait for response to query beofre timeout. |
| Last member query interval | Time between queries to determine the loss of the last member in an IGMP group. |
| Robustness value | Tolerance for lost packets. |
| LAN to LAN multicast | Allow multicast between LANs. |
| Max groups | Maximum allowed multicastgroups. |
| Max sources | Maximum allowed multicast sources. |
| Max members | Maximum allowed members in a multicast group. |
| Fast leave | Leave multicast groups immediately after the last host. |
| Join immediate | Join group directly. |
| Enable IGMP proxy | Turn on IGMP Proxy handling. |
| Ignore SSM Range | Ignore SSM and deliver regular multicasting. |
| IGMP snooping mode | IGMP snooping mode: Disabled / Standard / Blocking. |
| IGMP snooping interfaces | Interfaces to use for IGMP snooping. |
DHCP
The DHCP view lets you configure the DHCP server settings.
The DHCP settings are divided into several tabs.
Hostname Entries
The Hostname Entries tab allows you to configure hostnames for IPv4 or IPV6 addresses in the LAN.
General
The General tab allows you to configure the DHCP server basic settings.
Configuration
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Local domain | Local domain suffix appended to DHCP names and hosts file entries. | |
| Log queries | Write received DNS requests to system log. | |
| Leasefile | file where given DHCP leases will be stored. | |
| Ignore resolve file | Do not use the local Resolve file. | |
| Resolve file | Local DNS file storage. | File used by dnsmasq to find upstream name servers. |
| Ignore Hosts file | Do not use the local Hosts file. | |
| Hostname Entries file(s) | Path to additional host files to read for serving DNS responses. |
Advanced
The Advanced tab allows you to configure advanced settings for the DHCP server.
Configuration
| Item | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Domain required | Do not forward DHCP-requests without DNS-Name. | |
| Authoritative | This is the only DHCP in the local network. | |
| Filter private | Do not forward reverse lookups for local networks. | |
| Filter useless | Do not forward requests that cannot be answered by public name servers. | |
| Localise queries | Localise hostname depending on the requesting subnet if multiple IPs are available. | |
| Local server | Domain resolved from DHCP or hosts files only. | |
| Expand hosts | Add local domain suffix to names served from hosts files. | |
| No negative cache | Do not cache negative replies. | |
| Strict order | DHCP servers will be queried in the order of the resolve file. | |
| Bogus NX Domain Override | List of hosts that do not supply non-existent domain (NXDOMAIN) results. | |
| DNS forwarding | List of DNS servers to forward requests to. | |
| Rebind protection | Discard upstream RFC1918 responses. | |
| Allow localhost | Allow upstream responses in the 127.0.0.0/8 range. | |
| Domain whitelist | List of domains to allow RFC1918 responses to. | |
| DNS server port | Listening port for inbound DHCP queries. | |
| DNS query port | Fixed source port for outbound DNS queries. | |
| Max DHCP leases | Maximum allowed number of active DHCP leases. | |
| Max. EDNS0 packet size | Maximum size of EDNS0 UDP packets. | |
| Max. concurrent queries | Maximum number of concurrent DNS queries. |
Hostname Entries
The Hostname Entries tab allows you to configure hostnames for IPv4 or IPV6 addresses in the LAN.
Configuration
Add Hostname Entry
You can add as many entries as you like, and each entry can have any number of hostnames for each IP address.
To add a hostname entry:
- Click the Add button
- Click the Edit button
- Enter hostnames in the Hostname field
- Select address Family
- Enter IP Adress to redirect to
- Click Apply
Classifications
The Classifications tab lets you add classifications for connected clients.
The classifications can be used to provide specific DHCP Options options for the classified clients, based on client parameters.
Parameters
The classification can be based on client parameters:
- MAC class
View
At the top of the page is a list of configured classifications.
When a particular account is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
For all classification types, the configuration is similar:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Parameter value | Value for the classification parameter, according to its type. |
| Network ID | Option value. |
| ID | DHCP option ID. |
| Option | Option value. |
Add Tag
You can add as many tags as you like.
To add a tag:
- Click the Add button
The Select type of Classification dialog opens:
- Pick a Select Classification Type from the dropdown menu
- Click Apply
The tag is added to the list.
- Click the Edit button
- Enter Parameter value according to Classification Type
- Add as many DHCP options as needed:
- Click the Add option button
- Select the ID value
- Enter Option value
- Click Apply
SNMP
The SNMP Configuration view lets you configure the Simple Network Management Protocol service.
The SNMP settings are divided into tabs.
System
The System tab lets you configure general information about the SNMP service.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Physical location of the device. |
| Contact | Contact information for the responsible person. |
| Name | Name of the server. |
| Services | Offered services. |
| Description | Server description for presentation. |
| Object ID | Identifier for the device. |
Agent
The Agent tab allows you to manage SNMP agents.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Agent Address | Protocol and port for the agent variable. |
Add Agent
You can add as many agents as you like.
To add an agent:
- Click the Add button
- Enter an Agent Address
- Click Apply
Com2Sec
The Com2Sec tab lets you configure Com2Sec access profiles for the SNMP service.
Configuration
| Item | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Community | Community group to access. | private |
| Source | Hostname or subnet. | localhost |
| SecName | Access string. | rw |
Add Profile
You can add as many profiles as you like.
To add a profile:
- Click the Add button
- Enter parameters as needed
- Click Apply
Group
The Group tab allows you to configure Com2Sec access groups for the SNMP service.
Configuration
| Item | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Community | Community group to access. | public |
| Source | Hostname or subnet. | usm |
| SecName | Access string. | ro |
Add Group
You can add as many groups as you like.
To add a group:
- Click the Add button
- Enter parameters as needed
- Click Apply
View
The View tab lets you configure Com2Sec views for the SNMP service.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| View Name | Name of the view. |
| Type | Type of view. |
| OID | Object ID |
| Mask | Netmask. |
Add View
You can add as many views as you like.
To add a view:
- Click the Add button
- Enter parameters as needed
- Click Apply
Access
The Access tab allows you to configure Com2Sec access directives for the SNMP service.
Configuration
The access directive maps from group/security model/security level to a view.
| Item | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Group | Group. | |
| Context | Security name or empty. | |
| Version | Version access. | any / v1 / v2c / usm |
| Level | Access level. | noauth / auth / priv |
| Prefix | Context matching. | exact / prefix |
| Read | Read permissions | |
| Write | Write permissions | |
| Notify | Notify permissions. |
Add Access Group
You can add as many acces groups as you like.
To add an access group:
- Click the Add button
- Enter parameters as needed
- Click Apply
Pass
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Persist | Enable permanent passthrough. |
| Priority | Passthrough priority. |
| MIB OID | Object ID for the MIB. |
| Program | Execution for the arguments. |
Add Passthrough
You can add as many passthroughs as you like.
To add a passthrough:
- Click the Add button
- Enter parameters as needed
- Click Apply
Samba
In the Samba view you can change settings for the Sambaserver.
The Samba settings are divided into sections.
General
The General section of the view allows you to change the general Samba settings, such as name, workgroup and interface.
General
The General section of the view allows you to change the general Samba settings, such as name, workgroup and interface.
Configuration
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Service identifier. |
| Workgroup | Service workgroup. |
| Description | Description of the service. |
| Interface | Interfaces to provide the service to. |
Change Interface Settings
To change the interface that Samba will listen on:
- Click LAN to open the list
- Choose as many interfaces as needed
- Click outside of the list
- Click Apply
Samba Users
The Samba Users section of the view allows you to change the user settings.
Configuration
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Username | user name |
| Password | password |
| Description | description |
Samba User Settings
To add a Samba user:
- Click Add
- Edit the parameters as needed.
- Click Apply
WIFI
The WiFi view shows you information about your wireless network.
Overview
WPS Settings
The WPS Settings view lets you change the default wireless security settings (WPS) to make your network more secure.
MAC Filter
In the MAC Filter view you can make your wireless network more secure. Just specify which devices are allowed to connect, or explicitly lock out devices.
General
In the General WiFi view you can view and edit the wireless interface.
Overview
Wireless
In the Wireless view you can view and edit the wireless interfaces.
Each radio can have up to 4 SSIDs.
Radios
The Wireless Radios view allows you to configure wireless radios installed on your system.
At the top of the page is a list of radios.
Clicking the Edit button will open the edit view for that radio.
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| Radio On/off | Turn radio on or off. |
| WiFi Mode (SSID) | Choose wifi mode. |
| Channel | Choose WiFi Channel. |
| Bandwidth | Choose bandwidth. |
| Scan Timer | Determine the dwell time for channel hopping. |
| DFS Channels | Turn DFS channels on or off. |
| Beamforming | Turn beamforming on or off. |
| Airtime Fairness | Turn ATF on or off. |
| Maximum Associated Stations | Maximum number of clients allowed. |
| RX Chain PowerSave Quiet Time | Turn RXC PS Quiet Time on or off. |
| RX Chain PowerSave PPS | Turn RXC PS PPS on or off one of the receive chains to save power. |
| Enable WMM Multimedia Extensions | Turn WMM multimedia extensions on or off. |
| Disable WMM Ack | Turn WMM acknowledgement on or off. |
| Enable WMM UAPSD Power Saving | Turn WMM UAPSD power saving on or off. |
Wireless
In the Wireless view you can view and edit the wireless interfaces.
Each radio can have up to 4 SSIDs.
Configuration
At the top of the page is a list of selectable interfaces.
When a interface is selected, the edit view for the interface is shown below.
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn on or off. |
| WiFi Network Name | Edit name of SSID network. |
| Broadcast SSID | Toggle to make network visible or invisible. |
| AP isolation | Toggle to turn access point isolation on or off. |
| Wireless Multicast Forwarding | Toggle to turn multicast forwarding on or off. |
| Maximum Number of Connected Clients | Maximum number of connected clients. |
| Encryption | Change to a different encryption method. |
| Cipher | Choose form of Cipher. |
| WiFi Key (Password) | Reset to default password. |
| Show Key Text | Change format of wifi key text. |
Add Wireless Interface
Band Steering
The Band Steering view allows you to enable and configure band steering for the device.
Configuration
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| Enable | Turn band steering on or off. |
| Steering Policy | RSSI or bandwidth. |
| Threshold | Bandwidth or RSSI threshold value. |
Enable Band Steering
To enable band steering:
- Click Enable toggle
- Choose steering policy
- Set threshold value to use for the selected policy.
AP Steering
The Access Point Steering view allows you to enable and configure AP Steering for the device.
Note: This feature is only enabled if the device discovers another Inteno device in the same network.
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | Turn AP steering on or off. | |
| RSSI Threshold | Deauthentication RSSI threshold value. | Client will be de-authenticated if RSSI goes below this value. |
| Reassoc Timer | Grace period in seconds. | Clients returning below the RSSI threshold are immune from de-authentication until after Retry Interval. |
| Retry Interval | Timeout period in seconds. | After this time, the client can be de-authenticated. |
Enable AP Steering
To enable AP Steering:
- Click Enable toggle
- Set Threshold value
- Set Reassociation timer value
- Set Retry Interval value
WPS Settings
The WPS Settings view lets you change the default wireless security settings (WPS) to make your network more secure.
Overview
General WPS Settings
The WPS Settings section allows you to choose and configure different connection methods on an encrypted channel.
WPS-PBC: Push Button on Device
The WPS-PBC: Push Button on Device section lets you pair your devices.
WPS/REG: Device provides PIN
The section WPS-REG: Device provides PIN lets you generate a personal identification number through WPS.
WPS-PIN: Another Device provides PIN
The section WPS-PIN: Another Device provides PIN allows you to enter a PIN provided by another device.
WPS-PIN: Another Device provides PIN
The section WPS-PIN: Another Device provides PIN allows you to enter a PIN provided by another device.
Configuration
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| Enter your device PIN | Enter device PIN |
| Pair (within 2 minutes) | Pair button. |
WPS/REG: Device provides PIN
The section WPS-REG: Device provides PIN lets you generate a personal identification number through WPS.
Configuration
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| WPS Using Generated PIN | Turn on or off. |
| Generated PIN | Generated PIN shown |
| Generate PIN | Generate button. |
Generating a PIN
To generate a PIN through WPS:
- Click the Generate button
General WPS Settings
The WPS Settings section allows you to choose and configure different connection methods on an encrypted channel.
Configuration
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| WPS Function | Turn on or off for device. |
| Enable WPS on (5GHz) | Turn WPS on or off for radio. |
| Enable WPS on (2.4GHz) | Turn WPS on or off for radio. |
WPS-PBC: Push Button on Device
The WPS-PBC: Push Button on Device section lets you pair your devices.
Configuration
| Item | Comment |
|---|---|
| Enable WPS button on device | Turn on or off. |
| Pressing WiFi on/off button on your device for long time activates pairing | Turn on or off. |
| Pair (within 2 minutes) | Pair button. |
Pairing Your Device
To a device via WPS:
- Click the Pair button
- Press the corresponding button on the device you wish to connect
Your device will be open for pairing for two minutes.
MAC Filter
In the MAC Filter view you can make your wireless network more secure. Just specify which devices are allowed to connect, or explicitly lock out devices.
Configuration
Filters can be applied separately for each radio .
The devices are identified by their MAC address. You can manage up to 32 devices.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| MAC Filtering | Turn filtering on or off. |
| Access for listed devices | Access setting for clients in the list. |
| Currently added devices | List of filtered devices. |
| Add currently connected hosts ot the list | Collect all currently active devices to the list. |
Enable MAC Filter
To enable MAC Filtering:
- Click the MAC Filtering toggle button
- Choose type of Access for listed devices
- Allow - Access
- Deny - No access
- Click the
 add button next to Currently added devices
add button next to Currently added devices
- Enter the MAC address for the device
- Click Save
- Click Apply
System
The System view provides access to device information, management, provisioning and settings.
Overview
General Settings
The General Settings view contains basic device settings.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Local Time | Local time for the device. |
| Timezone | Device timezone setting. |
| Hostname | Device hostname. |
Firmware Upgrade
The Firmware Upgrade view lets you upgrade the device firmware by using image files.
IUP
The IUP view allows you to set up parameters for provisioning services and configurations with Inteno Universal Provisioning.
TR69
The TR69 Settings view allows you to configure TR069 support for device management and provisioning from the WAN.
Power Management
The Power Management view allows you to manage CPU effiency and Ethernet hardware ports.
General Settings
The General Settings view contains basic device settings.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Local Time | Local time for the device. |
| Timezone | Device timezone setting. |
| Hostname | Device hostname. |
Time Servers
The Time Servers section shows NTP time servers in use.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Time Servers (NTP) | List of NTP servers to use. |
| Server Mode | Turn NTP server mode on or off. |
Add Server
To add a time server:
- Click the
 add button
add button
- Enter the server address in URL box
- Click Apply
Log Settings
The Log Settings view contains settings for the system logs.
Current Firmware
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| System Log Level | System Logging level |
| Cron Log Level | Cron Logging level |
| Kernel Log Level | Kernel Logging level |
| Log File | Location to save the log file. |
| Log IP | IP address of remote log server. |
| Log Port | Port for the remote log server. |
| Log Prefix | Prefix to use in log. |
| Log Protocol | Protocol for transfer of log information (UDP / TCP). |
| Log Remote | Turn remote logging on or off. |
| Log Size | Max size of log in Kb. |
| Trailing null | Use trailing null insted of newline when using TCP |
| Log Type | Type of logging to use (circular = limited /file = unlimited number of files). |
Connectivity Test
The Connectivity Test view allows for automatic verification of the Internet connection by accessing a predefined URL.
Current Firmware
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Internet | URL for checking Internet connection. |
Passwords
The Passwords view lets you change passwords for device users.
Change Password Dialog
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Current Password | The existing password. |
| New Password | Password to change to. |
| Reenter Password | Verification of new password. |
| Password Strength | Indicates the security level of the new password. |
Note: For security reasons, the current password is never displayed.
Change password
To change password for a user:
- Open the Change password for user
- Select a user role
- Click Change Password
The change password dialog opens.
- Enter the current password
- Enter the new password
- Enter the new password again
- Click Change Password
Firmware Upgrade
The Firmware Upgrade view lets you upgrade the device firmware by using image files.
Current Firmware
The Current Firmware Version shows currently installed firmware on the device.
Online Update
With the Online Update function, you can perform an automatic search for upgrade image file on an upgrade server.
Note: The type of image file and server adddress and to use for upgrades is defined in Firmware options.
USB Firmware Upgrade
In the USB Firmware Upgrade section you can perform an automatic search for upgrade image file on USB devices, and perform the upgrade.
The check for upgrade starts a search for image files on any connected USB devices.
Note: The type of image file to use for upgrades is defined in Firmware options.
Manual Firmware Upgrade
In the manual firmware upgrade section you can select an image file on your computer, upload it to the device, and perform the upgrade.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Select firmware file to upload | Upgrade image file on local computer. |
| Start upgrade | Button to start upgrade. |
Backup/Restore
The Backup/Restore view allows you to manage backups and resets of the device.
Overview
Backup Configuration
In the Backup Configuration section you can save a copy of your device configuration or load a saved configuration into the device.
Backup Settings
The Backup Settings view lets you select which services and settings to include in backups.
Backup Configuration
In the Backup Configuration section you can save a copy of your device configuration or load a saved configuration into the device.
Save Backup
- Click Save
The Save Configuration dialog opens.
- If you want to encrypt the backup file:
- Click the Password Protection slider
- Enter a Backup file password
- Retype the password
- Click Continue
The file is saved as a compressed file archive to your local computer.
Load Backup
To load a saved configuration after the factory reset:
- Click Load
The Load New Configuration dialog opens.
- Click Choose File
- If the backup file is encrypted:
- Enter a Backup file password
- Click Continue
Factory Reset
In the Factory Reset section you can restore the device to factory settings.
Soft Reset
Alternatively, you can choose to perform a Soft Reset, where you select particular settings to keep when doing the factory reset.
Note: Reset restores your device to the factory defaults and removes any configurations you have made. You can only keep settings if you select them in the Soft Reset section.
Available Settings
These are the settings you can protect:
| Settings | |
|---|---|
| Port redirects | |
| Parental rules | |
| User password | |
| ICE config | |
| WiFi Settings |
Soft Reset
To perform a soft reset:
- Select the settings you want to keep:
- Click the Soft Reset slider button
- Make sure that the settings you want to keep are enabled.
Note: Enabled settings will be protected from the factory reset.
- Click Reset
Factory Reset
To perform the factory reset:
- Click Reset
Backup Settings
The Backup Settings view lets you select which services and settings to include in backups.
The list contains a selection of services and settings that can be included when performing backups.
You can change the status of any item by moving the associated slider.
IUP
The IUP view allows you to set up parameters for provisioning services and configurations with Inteno Universal Provisioning.
Configuration
The IUP view is divided into several sections.
General
In the General section you can manage general provisioning settings.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn provisioning on or off. |
| Update frequency start time | Time of day to start update. |
| Update frequency | Hourly / Daily / Weekly. |
| Export file | Download provisioning file. |
Main Provisioning Server
In the Main Provisioning Server section you can add a manual provisioning server address.
Note: This will override DHCP Discover Provisioning, even if it is enabled.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Reboot | Reboot after configuration has been applied. |
| Keep user config | Address to the provisioning server. |
| Enabled | Turn main provisioning server on or off. |
DHCP Discover Provisioning Server
In the DHCP Discover Provisioning Server section you can enable automatic discovery of provisioning server.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn software update on or off. |
Software Update Config
In the Software Update Config section you can configure online update of software.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn software update on or off. |
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Turn software update on or off. |
| Default reset | Remove device configurations and set to default. |
| Software URL | Location of software configuration. |
Sub Configs
In the sub configs section you can add sub configurations of specific parts.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| URL | Location of configuration file. |
| Package Control | |
| Enabled | Turn sub configurations on or off. |
Add Sub Config
To add a sub configuration:
- Click Add sub config
- Enter the URL for the configuration file
- Enter the relevant Package Control
- Select if the sub config should be Enabled
TR69
The TR69 Settings view allows you to configure TR069 support for device management and provisioning from the WAN.
The TR69 view is divided into sections.
Configure ACS Specific Settings
In the ACS section, you can configure ACS settings.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| ACS User Name | User name for the ACS connection. |
| ACS Password | Password for the ACS connection. |
| URL | Location of the ACS server. |
| Periodic Inform Enable | Turn Periodic Inform on or off. |
| Periodic Inform Interval | Wait time between Periodic Inform calls for CPEs. |
| DHCP Discovery | Turn automatic discovery of server on or off. |
Configure CPE Specific Settings
In the CPE section, you can configure CPE connection settings.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| WAN Interface | Interface for the connection. |
| Connection Request User Name | User name for the ACS connection |
| Connection Request Password | Password for the ACS connection. |
| Port | Specific connection port. |
| Log Severity Level | Logging information level. |
| Log to console | Display logging messages in the console. |
| Log to file | Turn logging to file on or off. |
| Log file max size | Size of log file. |
| Provisioning Code | Identifier for provisioning. |
ICE
The ICE view allows you to configure ICE support for device management and provisioning from the WAN.
Configuration
| Item | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| ICE | ||
| Enabled | Turn ICE communication engine on or off. | If ICE is disabled, Cloud is disabled automatically. |
| Cloud | ||
| Status | Current status for the cloud service. | Offline /Registered |
| Enabled | Turn Cloud service on or off. | Enables the XMPP connection to the Cloud URL. |
| Cloud URL | URL for access to the the device. | |
Management
The Management view lets you configure WAN to SSH connections and access to services.
Overview
Services
The Services view lets you configure WAN access to device services, if your device has this capability.
OWSD
The OWSD view lets you configure settings for the open web-server daemon.
The server listens on a number of interfaces, and allows for separate configuration of access for each of them.
At the top of the page is a list of interfaces the server listens on.
When a particular interface is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
Configuration
The Configure firewall rule section allows you to enable and configure a firewall rule for the selected service.
Add Listen Interface
- Click Add
- Enter a Name
The firewall settings are displayed.
- Add interface settings as needed.
- Click Apply
Add Origin
Select an interface in the list.
- Click Add
- Enter the Origin
- Click Add
- Click Apply
SSH
The SSH view allows you to configure SSH access, server instances, and keys.
Dropbear Instances
The Dropbear Instances section lets you create SSH server instances with different parameters.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Password Autentication | Turn access with password authentication on or off. |
| Port | Connection port. |
| Enable Root Password Auth | Turn root access with password authentication on or off. |
| Enable Root Login | Turn root account access on or off. |
| Enable Forwarded Ports | Turn forwarded ports on or off. |
| Interface | Restrict SSH server to particular interface. |
Add SSH Server instance:
To add a SSH Server instance:
- Click Add
- Enter parameters for the instance
- Click Apply
Accepted SSH Keys
The SSH view allows you to configure SSH access, server instances, and keys.
Add Key
To add a SSH key:
- Click Add
- Copy the public SSH key
- Paste the public SSH key into the window
- Click OK
- Click Apply
CATV
The CATV view lets you enable the CATV service, if your device has this capability.
Configure
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Ebnable | Turn CATV / RF Enable on or off. |
Services
The Services view lets you configure WAN access to device services, if your device has this capability.
Allow WAN Access To Running Services
At the top of the page is a list of services.
When a particular service is selected, details about it is shown in the configuration section.
Configure firewall rule for this service
The Configure firewall rule section allows you to enable and configure a firewall rule for the selected service.
Where applicable, the configuration is divided into separate sections for source and destination zones.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable WAN forwarding for this service | Turn WAN access on or off. |
| Name | Identifier for the rule. |
| Zone | Device / Any / LAN / WAN |
| IP | IPv4 / IPv6 address. |
| MAC | MAC address. |
| Port | Port affected. |
| IP version | Any / IPv4 / IPv6 |
| Protocol | Protocol affected: (UDP / TCP / ICMP / TCP + UDP / ESP) |
| Firewall action | Firewall action to perform. |
Add Firewall Rule
Select a service in the list.
- Click the Enable WAN forwarding for this service button
The firewall settings are displayed.
- Add rule settings as needed.
- Click Apply
LEDs
The LED view allows you to enable or disable the status LEDs on your device.
Displayed Leds
The exact LEDs available vary with device type. The status of each LED is shown on the left of the name.
Examples
BROADBAND
DECT
DSL
EXT
INTERNET
LOGO
STATUS
VOICE1
WAN
WIFI
WPS
Toggle LED
To switch a LED on or off:
- Find the desired LED in the list
- Click the slider button in the interface
- Click Apply
Power Management
The Power Management view allows you to manage CPU effiency and Ethernet hardware ports.
Configuration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| CPU Speed | CPU Sync. |
| CPU r4k Wait | Sleep mode configuration. |
| Ethernet Auto Power Down | Turn Ethernet Auto Power Down on or off. |
| Energy Efficent Ethernet | Turn Energy-Efficient Ethernet on or off. |
Services
The Services view lets you manage system services on the device.
Configuration
The list contains system running and available services.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Priority | System priority. |
| Service | Service identifier. |
| Enable | Enable or disable service. |
| Action | Buttons to start, stop and restart the service. |
Restart
The Restart page allows to restart your Internet connection and reboot your device.
Restart device
Note: Restarting the device will disconnect all phone, Internet and TV services while the device is restarting.
To restart your device:
- Click Restart
A confirmation dialog is shown
- Click Yes
A restart dialog is shown.
When the device has restarted, the browser reconnects and the login dialog is shown.
Status
The Status area provides an overview of the current situation for your device, network and services, and also contains diagnostic tools.
Overview
System
The System Status view displays information about a number of parameters regarding your gateway and its operation.
IGPM TV
The IGPM TV Status views shows information about your IPTV services and their connection status.
WiFi
The WiFi Status view shows information about the wireless network, and allows you to scan the local area for other wireless access points.
USB
The USB devices views displays information about any USB devices connected to the gateway device.
Note: Supported file systems for USB devices are NTFS and FAT32.
Voice
The Voice Status view shows information about SIP accounts, phone numbers and voice lines connected to the device.
System
The System Status view displays information about a number of parameters regarding your gateway and its operation.
Overview
System
The System Status overview shows basic data about the device.
Configuration
| Option | Description | Sample value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hostname | The hostname for the gateway. | Inteno | |
| Model | Gateway model. | DG400A | |
| Serial No | Device serial number. | G542012033 | |
| MAC Address | Device MAC address. | 00:22:07:A9:CE:F9 | |
| Filesystem | Filesystem used in gateway storage. | UBIFS | |
| Firmware Version | Version of installed firmware. | DG400-WU7U_INT3.5.5-160513_1617 | |
| Other Bank | Alternative firmware. | DG400-WU7U_INT3.13-170904_1354 | |
| Kernel Version | The gateway operating system kernel version. | 3.13 | |
| BRCM Version | (Broadcom Devices only) Version number for the Broadcom driver. | 4.16L.04 | |
| CFE Version | Version of CFE. | 4.16L.05 | |
| Local Time | Time according to the gateway internal clock. | Mon May 23 2049 17:21:12 GMT+0200 (CEST) |
| Uptime | Time the gateway has been runnning since last startup. | 5d 2h 53m 14s |
| CPU | Percentage of CPU processing in use. | 0% |
| Active Connections | Number and percentage of connections to the gateway. | 259 / 7660 (3%)` |
System Memory
The System Memory Status view displays information about memory usage in the device.
Configuration
| Option | Description | Sample value |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Memory used by the system. | 163144 kB / 226308 kB (72%) |
| Shared | Shared memory in use. | 0 kB / 226308 kB (0%) |
| Buffered | Memory buffer in use. | 0 kB / 226308 kB (0%) |
| Swap | Swap file system used. | 0 kB / 0 kB (0%) |
System Storage
The System Storage Status view shows information about file systems and space used.
Examples
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| rootfs(/) | Root. |
| tmpfs(/tmp) | Temporary. |
| tmpfs(/dev) | Devices. |
| tmpfs(/mnt) | Mount point. |
| tmpfs(/dev/sda1) | An attached USB stick. |
Processes
The Processes view shows information about system processes and CPU usage.
Overview
The overview shows a summary of the processes:
| Item | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Total number of processes | 96 | |
| Total CPU usage | 9% |
Process Detail Toggle
You can access detailed realtime information about running processes, by clicking the information toggle.
To open the Details view:
- Click Click here to view details
Details
In the details view, you can get detailed information about all processes running on the device.
Configuration
For each process, information about a number of properties is displayed:
| Property | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| PID | Process ID | Unique identifier for the process. |
| PPID | Parent Process ID | Unique identifier for the parent process. |
| USER | User running the service. | |
| STAT | State Code. | |
| VSZ | Virtual Memory Size. | |
| VSZP | Virtual Memory Size Percentage. | |
| CPU | CPU Percentage. | |
| COMMAND | The command used to run the process. |
Network
The Network Status view shows information about various aspects of your network.
Overview
Routing Tables / Status
The Routing Status view shows the static routes configuration for the various network types.
Status
The Network Status view provides an overview of network elements for your device.
Configuration
WAN6
The WAN6 view shows information about any connected IPv6 network.
LAN
The LAN view shows information about the local network connected IPv4 network.
| Option | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| IP Address | IP address of the device on the local network. | Typically 192.168.1.1. |
WAN
The WAN view shows information about any connected IPv4 network.
| Option | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| IP Address | IP address for the device on the Internet. | |
| Gateway | IP address to the internet gateway. | |
| Primary DNS | First priority DNS server. | |
| Secondary DNS | Second priority DNS server. |
Clients
The Connected Clients view shows a list of clients connected to the network.
Table
| Column | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Hostname | Client hostname. | |
| MAC Address | Client MAC Address . | |
| IPv4 Address | Client IPv4. | |
| IPv6 Address | Client IPv6 address. | |
| Active Connections | Number of active connections. |
Routing Tables / Status
The Routing Status view shows the static routes configuration for the various network types.
Overview
IPv6 Neighbors
The IPv6 Neighbors view shows information about IPv6 devices in the network neighborhood.
ARP
The ARP status view shows information about ARP routes.
Table
The table displays information about static ARP routes.
| Column | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | IPv4. | |
| MAC Address | Client MAC Address . | |
| Device | Network device type. | Displayed as virtual interface name. |
IPv4
The IPv4 status view shows information about IPv4 routes.
Table
The table displays information about static IPv4 routes.
| Column | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| IPv4 Address | IPv4. | |
| Gateway | IP address to the internet gateway. | |
| Genmask | Route genmask. | |
| Device | Network device type. | Displayed as virtual interface name. |
IPv6
The IPv6 status view shows information about IPv6 routes.
Table
The table displays information about static IPv6 routes.
| Column | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| IPv6 Address | IPv6 address. | |
| Next Hop | Next Hop device. | |
| Device | Network device type. | Displayed as virtual interface name. |
IPv6 Neighbors
The IPv6 Neighbors view shows information about IPv6 devices in the network neighborhood.
Table
The table shows information about discovered IPv6 neighbors.
| Column | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| IPv6 Address | IPv6 address. | |
| IPv6 Status | Device status. | INCOMPLETE / REACHABLE / STALE / DELAY / PROBE |
| Device | Connected device. | |
| MAC address | MAC address for the device. | |
| Router | Is the device a router? | true/false |
NDP Status
The RFC 4861 defines a number of statuses:
| Status | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
INCOMPLETE | Address resolution is in progress and the link-layer address of the device has not yet been determined. | |
REACHABLE | Device is known to have been reachable recently (within tens of seconds ago). | |
STALE | Device is no longer known to be reachable but until traffic is sent to the neighbor, no attempt should be made to verify its reachability. | |
DELAY | Device is no longer known to be reachable, and traffic has recently been sent to the neighbor. Probes should be delayed in order to give upper-layer protocols a chance to provide reachability confirmation. | |
PROBE | Device is no longer known to be reachable, and unicast Neighbor Solicitation probes are being sent to verify reachability. |
DHCP
The Active DHCP Leases view shows the status of any DHCP leases currently in use.
DHCPv4 Leases
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Hostname | Client hostname. |
| IPv4 Address | Client IPv4. |
| MAC Address | Client MAC Address. |
| Leasetime remaining | Time until the lease expires. |
DHCPv6 Leases
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Hostname | Client hostname. |
| IPv6 Address | Client IPv6 address. |
| DUID | Client DUID. |
| Leasetime remaining | Time until the lease expires. |
NAT
The NAT view shows a list of active NAT mappings in the device network.
Connections
The Active Connections gauge shows how many NAT mappings are in use out of the allowed total, as a percentage and as a count.
NAT Connection Table
Connections to and from the local network to the external network are added to the table, allowing the device to handle traffic routing decisions.
The table displays information about active NAT connections.
| Column | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | Communication protocol used. | |
| Source | Internal IP address. | |
| Destination. | External IP address. | |
| Source Port | Internal Port. | |
| Destination Port | External Port. |
WiFi
The WiFi Status view shows information about the wireless network, and allows you to scan the local area for other wireless access points.
Overview
General
The general WiFI Status view displays information about your wireless channels and network interfaces.
WiFi Scan
The WiFi scan view allows you to scan the area around the device to find out what other access points are visible.
General
The general WiFI Status view displays information about your wireless channels and network interfaces.
Configuration
For each wireless radioinformation is displayed about:
- WiFi channel in use.
- Noise level in dB for the channel.
- WiFi interface name.
- WiFi encryption used by the interface.
Client
For each connected client, more infomation about the connected client is available.
Details
To view more details about a client, click the expand button.
| Item | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| IP-Address | Client IPv4 address. | 10.0.0.154 |
| MAC-Address | Client MAC address. | 1A:97:1C:C7:76:63 |
| DHCP | Does client use DHCP? | true |
| Idle | Is the device transmitting? | 0 |
| In Network | ID for connected network. | 74 |
| RSSI | Received signal strength indicator value. | -42 dBm |
| SNR | Signal to Noise Ratio value. | 41 dB |
| Number of Antennas | Client antennas in use. | 2 |
| TX Rate | Transmission rate. | 130 Mbps |
| RX Rate | Receive rate. | 144 Mbps |
| Flags | Provided device flags. | BRCM, WME, N_CAP, AMPDU |
| HT Capabilities | Supported HT Capabilities (data rates). | LDPC, BW40, SGI20, SGI40 |
| TX Total Packets | Total number of transmitted packets. | 22589 |
| Unicast Packets | Total packets transmitted through unicast. | 224 |
| TX Unicast Packets | Packets transmitted through unicast. | 224 |
| TX Multicast/Broadcast Packets | Packets transmitted through multicast. | 22365 |
| TX Failures | Transmission failures. | 0 |
| RX Data Packets | Received packets. | 440 |
| RX Unicast Packets | Received packets transmitted through unicast. | 209 |
| RX Multicast/Broadcast Packets | Received packets transmitted through multicast. | 231 |
| TX Data Packets Retried | Resent data packets. | 0 |
| TX Total Packets Sent | Total data packets transmitted through unicast. | 7 |
| TX Packets Retries | Retransmitted data packets. | 1 |
| TX Packets Retry Exhausted | Data Packets failed after retry. | 0 |
| RX Total Packets Retried | Retransmitted data packets. | 107 |
Utilization
The WiFi Utilization view displays information about usage for the connected devices in the network.
Table
Each available radio is displayed in a table, with one client per row.
WiFi Scan
The WiFi scan view allows you to scan the area around the device to find out what other access points are visible.
Chart
The scan results table displays all detected access points and information about each in a graphical manner.
Axes
The horizontal axis shows the discovered channels.
The vertical axis shows the signal strength, according to RSSI.
| Color | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Red | Poor. | |
| Yellow | Acceptable. | |
| Green | Good. |
Table
The scan results table displays all detected access points and information about each:
| Column | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| SSID | SSID identifying the access point. | |
| Frequency | WiFi frequency band for the access point. | |
| Channel | Channel used by the access point. | |
| RSSI | RSSI strength for the signal. | |
| Noise | Noise level for the connection to the access point. | |
| Cipher | Cipher used for encryption in the access point. | |
| WPS | WPS version used by the access point. |
Scan WiFi
To scan a frequency band:
- Select Frequency to Scan
- Click Scan
The results for the selected band are displayed in the graph and table.
Band Steering
The Band Steering view shows information about band steering.
Status
The status section shows the current band steering status.
The information is displayed in the STA info summary table.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| STAMAC | Station (client) MAC address. | | Interface | Client interface name. | | TimeStamp | Timestamp for the steering event. | | Txrate | Transmission rate. |
| RSSI | Received signal strength indicator . |
| Bounce | Does the client bounce back to a particular bandafter steering? (yes/no). |
| Picky | Does the client prefer a particular band? (yes/no). |
| PSTA | Is the client a proxy station? (yes/no). |
| DUALBAND | Is the client dual-band capable? (yes/no). |
Log
The log section contains the log file, which shows the band steering events.
The information is displayed in the Band Steering Record table.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Seq | |
| TimeStamp | Timestamp for the steering event. |
| STAMAC | Station (client) MAC address. | | Fmch | From channel (hex code). |
| To_ch | To channel (hex code). |
| Reason | Event (hex code). |
| Description | Description of event. |
DSL
The DSL status view shows information about any DSL connections to the device.
DSL Status Information
The DSL Status Information section shows the status for the DSL line.
Line Status
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Idle | No connection. |
| Handshake | Searching for connection, negotiating transfer. |
| Training | Connection found, testing cable. |
| Showtime/Active | Connection established. |
DSL Mode
The DSL Mode section shows the DSL.
Bit Rate
The Bit Rate section shows transmission rates for streams in bits per second (bps).
Actual Data Rate
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Downstream | Rate to the device. |
| Upstream | Reate from the device. |
Operating Data
The Operating Data section shows signal strength for the DSL line.
SNR margin
The SNR Margin section displays the signal-to-noise margin for the streams.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Downstream | To the device. |
| Upstream | From the device. |
Loop Attentuation
The Loop Attentuation section shows signal attentuation for the streams.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Downstream | To the device. |
| Upstream | From the device. |
Error Counter
The Error Counter section lists the number of (discovered) errors for the connection.
FEC Corrections
The FEC Corrections table shows FEC corrections for the streams.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Downstream | To the device. |
| Upstream | From the device. |
CRC Corrections
The CRC Corrections table shows CRC corrections for the streams.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Downstream | To the device. |
| Upstream | From the device. |
Cell Statistics
The Cell Statistics section shows the number of cells transmitted for the streams.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Received | To the device. |
| Transmitted | From the device. |
IGPM TV
The IGPM TV Status views shows information about your IPTV services and their connection status.
Configuration
The table shows any connected IGMP TV channels and information about each:
USB
The USB devices views displays information about any USB devices connected to the gateway device.
Note: Supported file systems for USB devices are NTFS and FAT32.
Table
The USB device information table shows information about the USB devices.
| Column | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Device ID | Identification for the USB device. | |
| Vendor ID | Identification for the manufacturer. | |
| Vendor Name | Name of the manufacturer. | |
| Device Name | Name reported by the USB device. |
CATV
The CATV Status view shows information about CATV services connected to the device.
Configuration
Note: Available on EG300 & EG400 only.
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Inteno model | Model. | CATV-302 |
| VPD | Reverse voltage on Protection Device. | -inf dBm |
| RF | Range. | 75.7 dBµV |
| RF enable | Enable RF. | OFF |
SFP
The SFP Status view shows information about SFP connectors enabled in the device.
Configuration
Information is shown in two tables; ROM information and DDM information.
Note: Available on EG300 & EG400 only.
DDM
The DDM table shows information about the DDM retrieved from the SFP.
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| voltage | Port voltage. | 3.1872 (V) |
| current | Port current. | 26.448 (mA) |
| tx-pwr | Broadcasting power. | 0.3530 (mW) |
| tx-pwr-dBm | Broadcasting power. | -4.5223 (dBm) |
| rx-pwr | Received signal power. | 0.3026 (mW) |
| rx-pwr-dBm | Received signal power. | -5.1913 (dBm) |
| rx-pwr-type | Received power type. | average |
ROM
The ROM table shows information about the ROM.
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| connector | Connector type. | SC |
| ethernet | Ethernet type. | LX |
| encoding | Encoding type. | 8B10B |
| rate | Line rate. | 1300 |
| single-mode | Single mode distance. | 20000 |
| vendor | Port manufacturer or vendor. | Skylane Optics |
| oui | Organizationally Unique Identifier. | 00:25:cd |
| pn | Product name. | SBU35020DR3D000 |
| rev | ROM Revision. | A |
| sn | Serial Number | b19bmjrx1857 |
| date | ROM date. | 2016-04-21 |
| ddm | DDM version | 9.3 |
Diagnostics
The Diagnostic Utility allows you to perform diagnostic tests from the web interface.
Overview
Speed Test
The Speed Test view allows you to perform a TP Test for your network, using your device as the endpoint.
Ping
The Ping Test view allows you to perform a Ping for a selected host.
Ping Test
To perform a ping test against an endpoint:
- Enter a valid hostname or IP address in the Host to ping box
- Click Ping
The result of the ping is shown below the utility.
Example:
PING 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: seq=0 ttl=64 time=0.208 ms 64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.130 ms 64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.129 ms 64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.146 ms 64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.130 ms --- 127.0.0.1 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 0.129/0.148/0.208 ms
Trace
The Tracing tool view allows you to perform a Traceroute Test for a selected host.
Traceroute Test
To perform a tracroute test against an endpoint:
- Enter a valid hostname or IP address in the Host to trace box
- Click Trace
The result of the trace is shown below the utility.
Example:
Trace results:
traceroute to 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1), 30 hops max, 38 byte packets 1 127.0.0.1 0.033 ms
Speed Test
The Speed Test view allows you to perform a TP Test for your network, using your device as the endpoint.
Configuration
| Option | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Direction | Traffic direction to test. | Up and Down, Up, Down. |
| Package Size | Size of test data packages to send. | Size of test packages to send. |
| Speedtest Server | Server to use for the test. | A number of default servers are provided, but you can edit the list. |
Perform Speed Test
Example
Test results:
Downstream: 103.45 Mbit/s Upstream: 44.10 Mbit/s
Add test server
If you have additional test servers you want to use, you can add them to the dropdown list.
To add a test server:
- Click the + plus sign
A dialog is shown allowing you to enter parameters:
- Add a valid Server Hostname
- Add a valid server Port
- Click OK
Remove test server
Servers in the test server list can be removed.
To remove a test server:
- Select the server in the Speedtest Server list
- Click the - minus sign
The server is removed from the list immediately.
Realtime Graphs
The Realtime Graphs view provides access to graphical representations of status for the device. The graphs scroll as time progresses and lines indicate the current status.
Overview
Load
The Load graph shows device load averages for different time recent periods.
Graph Lines
The display is shown in realtime, and the lines represent the average over different intervals:
| Color | Time |
|---|---|
| Blue | 1 minute |
| Red | 5 minutes |
| Purple | 15 minutes |
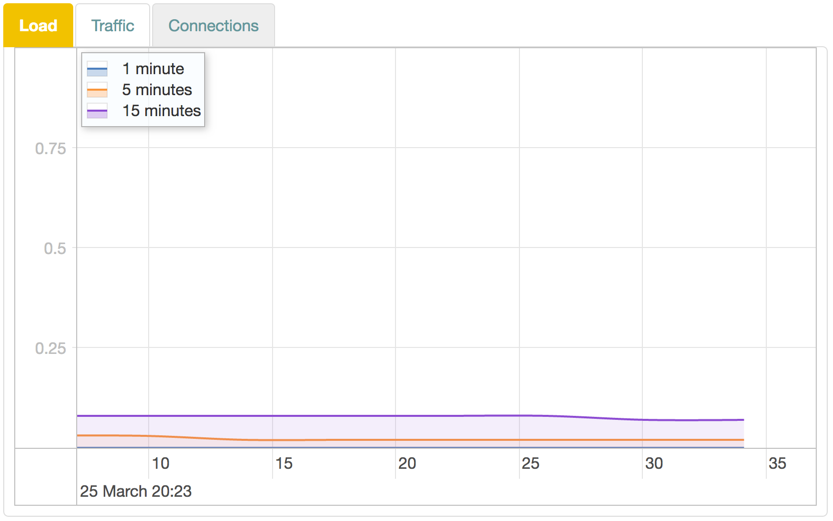
Traffic
The Traffic graph shows upload and download traffic for the interfaces.
Graph Lines
Each interface is available in its own tab. The display is shown in realtime, with lines representing traffic in kbit/s:
| Color | Traffic |
|---|---|
| Blue | Downstream. |
| Red | Upstream. |
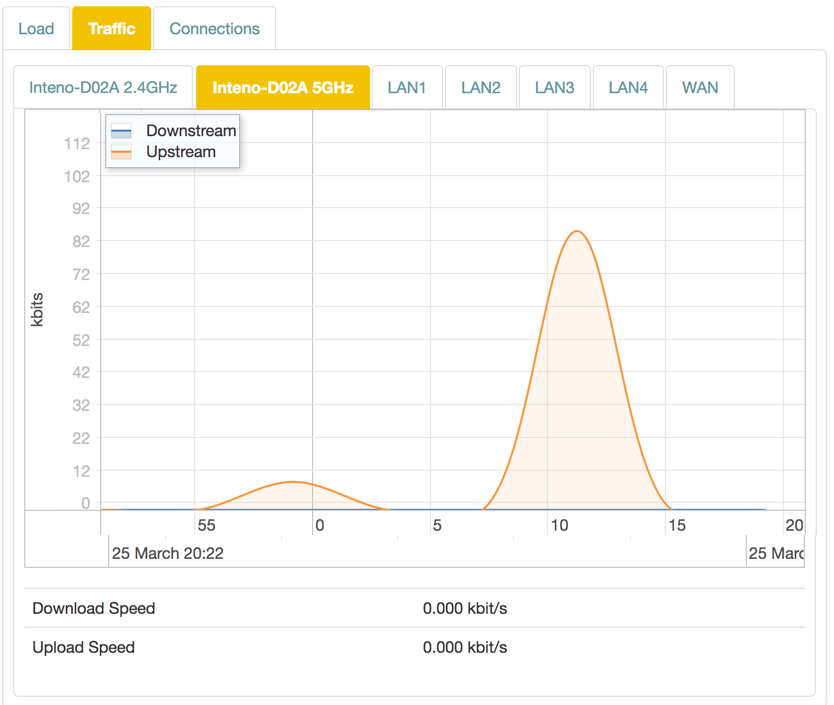
Connections
The Connections graph shows the number of currently active connections for the device.
Graph Lines
The lines representing different connection types:
| Color | Traffic |
|---|---|
| Blue | TCP connections. |
| Red | UDP connections. |
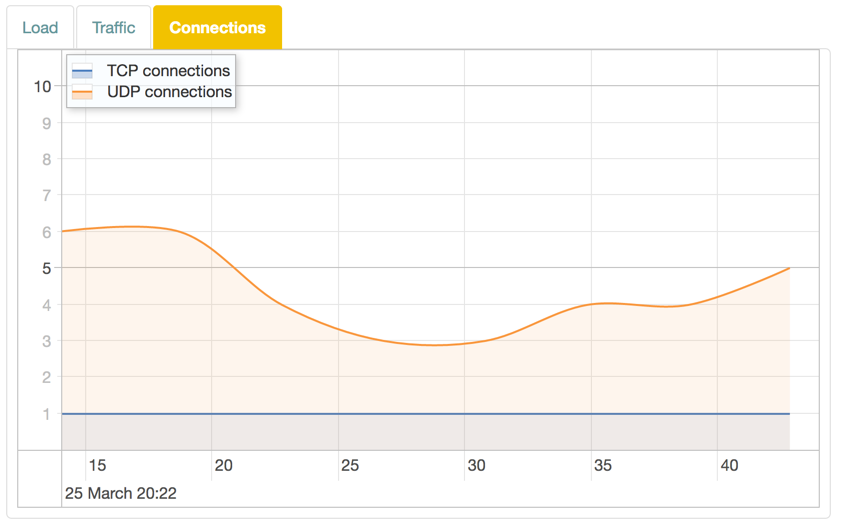
Voice
The Voice Status view shows information about SIP accounts, phone numbers and voice lines connected to the device.
Configuration
Information is shown in two tables.
Your phone numbers
| Option | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Name | SIP account name. | Uses type and number unless otherwise set. |
| User | SIP user. | |
| Domain | SIP domain. | |
| Registration interval | SIP registration interval domain. | |
| Last registration | Last registration time. | |
| Status | Current status of the line. |
Voice lines
The Voice lines shows a list of connected voice lines.
| Option | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Voice line name. | Uses type and number unless otherwise set. |
| State | Current state of the line. |
Event Log
The Event Log view lets you view and manage the event log for the device.
Log
The Log section contains log settings and lets you download the logs.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Download All Logs | Save the logs to the local computer. |
| Limit Log List | Limit the number of events. |
| Filter Log Messages By Source | Filter out events by freetext search in source. |
| Filter By Type | Filter out event types by Logging level. |
| Filter By | Filter out events in the log (firewall / network / system / iptv). |
Enable Online Help
For JUCI version 3.10.0+, online help is enabled by default.
However, if you upgrade from an earlier version, this option may not have been enabled. If so, you may need to connect to your device via SSH and run console commands to enable the setting.
CLI Enable Online Help
To enable online help:
Commands on Local Computer
- Open a console window on your local computer.
- Connect to the device:
ssh admin@192.168.1.1
Note: The address may be different from 192.168.1.1 for your device. Use the same address as for the usual login.
Note: You may need to enable SSH access to your device from the System > Management > SSH.
Note: For login, use the password defined in System > Passwords.
Commands on Device
The command line commands to run are the following:
To enable the help:
uci set juci.wiki.visible=1
To apply the setting:
uci commit juci